This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
MXene-enhanced plasmonic sensing developed for ultrasensitive label-free miRNA detection
A research group led by Prof. Yang Hui at the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has proposed an ultrasensitive MXene-enhanced plasmonic biosensor for real-time and label-free detection of microRNAs (miRNAs).
The study was published in Nanophotonics on Oct. 11.
As small non-coding RNA molecules, miRNAs play an important role in the development and progression of various types of cancer. The detection of miRNAs is significant to the early-stage diagnostics and prognostics because they can act as biomarkers.
However, due to their intrinsic characteristics, such as small size, short sequence length, low concentration levels and high sequence homology in complex real samples, traditional detection strategies for miRNAs are challenging.
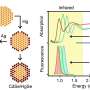
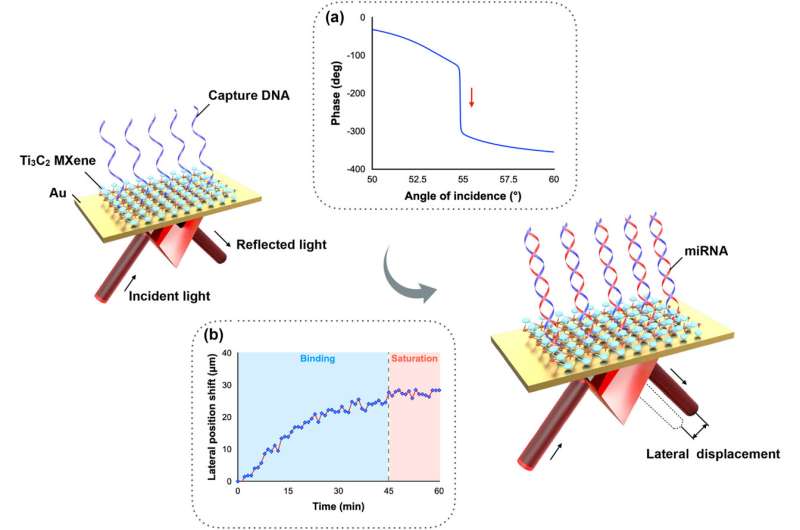
In this study, the researchers found that the reflectivity of the plasmonic substrate could be significantly reduced by spin-coating a thin layer of MXene nanosheets on it, resulting in a sharp phase change at the surface plasmon resonance angle. The sharp phase change would then induce a large lateral displacement signal and enhance the detection sensitivity.
Based on this biosensing approach, the researchers realized ultrasensitive detection of target miRNA with a detection limit as low as 10 fM. The sensing signal enabled the facile differentiation of the target miRNA from the single-base mismatched miRNA.
In addition, this plasmonic biosensor demonstrates the capacity to detect miRNAs in complex media, such as undiluted human serum samples, without compromising detection sensitivity.
"Our biosensing technique provides a promising tool for effective detection of miRNA. It can evolve into a platform to detect a wide class of nano-objects, such as many other tumor biomarkers in clinical diagnosis and viral particles," said Prof. Yang.
More information: Yuye Wang et al, Ultrasensitive label-free miRNA-21 detection based on MXene-enhanced plasmonic lateral displacement measurement, Nanophotonics (2023). DOI: 10.1515/nanoph-2023-0432
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences