This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
New technique enhances imaging of fluid-filled rocks, finds connection to microearthquakes
An international team of scientists led by Dr. Xin Liu, Assistant Professor of the Department of Earth Sciences, The University of Hong Kong (HKU), along with seismologists from the U.S. and China, has recently introduced a new method called ambient noise differential adjoint tomography, which allows researchers to better visualize rocks with fluids.
This could lead to potential advancements in the discovery of water and oil resources, as well as applications in urban geologic hazard and early warning systems for tsunamis and the understanding of the water cycle. Their findings have been published in Nature Communications.
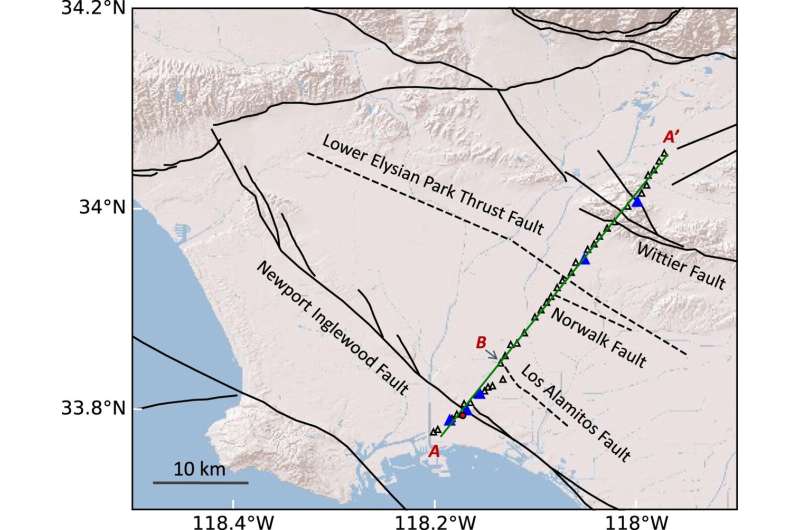
The method utilizes a portable instrument called a seismometer to record the Earths natural vibrations, making it a cost-effective and easy way to study areas in cities and oceans. Seismometers record ground motion in three dimensions: up–down, north–south, and east–west. In the study, 42 seismometers were placed along a line across the Los Angeles basin from Long Beach to Whittier Narrows.
Researchers found that rocks about 1–2 km beneath the surface near the Newport-Inglewood Fault, a fault that causes earthquakes, contain a significant amount of fluids. These rocks have tiny holes filled with fluids, which may explain the occurrence of small earthquakes in Long Beach, California. The abundance of fluids within these tiny holes reduces friction along the fault plane, allowing the two rock blocks on either side to slide past each other more easily and generate small earthquakes.
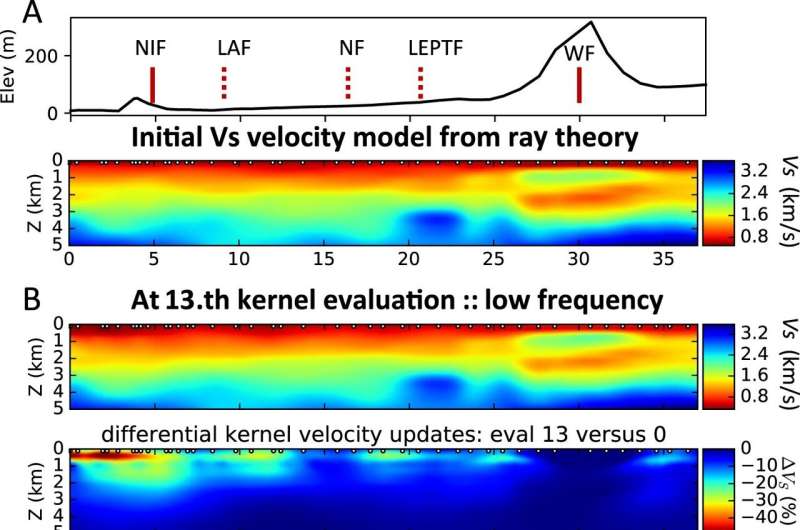
The paper suggests that ambient noise differential adjoint tomography can be used to find water and oil resources without the need for expensive drilling. This novel method generates images of the ground covered by seismometers, revealing how fast seismic waves travel in soils and rocks. In some locations, the seismic wave travels much slower compared to other regions at the same depth, indicating the presence of fluid. As water and oil are fluids in rocks, this method can identify rocks containing such fluids.
"Previously, groundwater aquifers or deep fluid reservoirs were difficult to find without drilling multiple expensive wells or costly seismic surveys with loud artificial sound that are not environmentally friendly on land or ocean. Using just weak seismic noise recordings by two dozen seismometers on land or seafloor, our new technique can create images containing fluid information within rocks, and pinpoint the location and depth of fluid-rich rocks," said Dr. Liu, who is also the first author of the journal paper.
Additionally, this innovative method can be used to create detailed images of the ground in urban areas and the deep ocean, serving various purposes such as assessing urban geologic hazards, implementing early warning systems for tsunamis and enhancing our understanding of the water cycle under the seafloor.
In urban settings, a series of land seismometers can be deployed over the area of interest. In the ocean, a line of Ocean Bottom Seismometers (OBS) can be installed on the seafloor to record background vibrations.
In both cases, a detailed image is created right underneath the line of seismometers, providing information about the locations of loose soil/sediments and fluid-bearing rocks that directly relate to regions with slow seismic wave velocity.
"In conclusion, this innovative method has the potential to revolutionize our approach to discovering and utilizing water and oil resources, enhancing urban safety measures, and deepening our understanding of the environment. Its direct impact on our daily lives spans from efficient resource exploration to effective disaster preparedness and promoting sustainable environmental management practices. This scientific breakthrough holds excellent promise in shaping a better future for us all," Dr. Liu added.
More information: Xin Liu et al, Ambient noise differential adjoint tomography reveals fluid-bearing rocks near active faults in Los Angeles, Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42536-4
Journal information: Nature Communications
Provided by The University of Hong Kong