This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Ice cores as a source for antimicrobials: From bioprospecting to biodesign

In November 2023, BioDesign Research published a perspective article titled "Ice Cores as a Source for Antimicrobials: From Bioprospecting to Biodesign," outlining a revolutionary approach to antibiotic discovery using ice cores. This innovative article comes at a pivotal time, as the golden age of antibiotic discovery has passed and the threat of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is looming, projected to cause 10 million deaths per year by 2050.
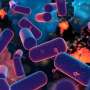
This study highlights the huge, untapped potential of ice cores, despite the reduction in antibiotic research by many pharmaceutical companies. These ice cores are biological time capsules that hold microorganisms and their genetic material, potentially for millennia. These microorganisms have developed unique antimicrobial compounds, which could be the key in the fight against AMR.
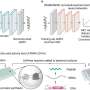
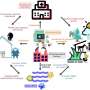
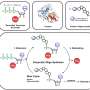
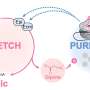
The biosynthesis approach involves bioprospecting of ice cores to unearth these ancient microbial life forms. Two complementary approaches, the ice core metagenomic analysis (ICEMAN) pipeline and synthetic biology techniques, are employed to maximize the discovery and optimization of new antibiotic compounds.
The ICEMAN pipeline includes a sequence-based protocol, Antibiotic Discovery and Analysis of Metagenomes (ADAM), and a laboratory culturing approach, Environmental Examination (EVE), ensuring a comprehensive search for potential antibiotics. Synthetic biology was then applied to optimize these compounds for efficacy against AMR.
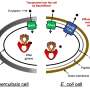
This includes innovative methods like phage display and outer membrane protein tethers, alongside advanced techniques in heterologous gene expression and metabolic engineering. However, the study also underscores the importance of biosafety and biosecurity. Given the age of these microorganisms, strict protocols are recommended to prevent environmental contamination and ensure public safety.
In conclusion, this article opens new avenues in the global fight against AMR, offering hope that ice cores may hold the key to the next generation of antibiotics. It not only presents a novel source of antimicrobial compounds but also exemplifies the synergy between traditional bioprospecting and modern synthetic biology, potentially leading to significant advancements in health care and medicine.
More information: Ying-Chiang Jeffrey Lee et al, Ice Cores as a Source for Antimicrobials: From Bioprospecting to Biodesign, BioDesign Research (2023). DOI: 10.34133/bdr.0024
Provided by NanJing Agricultural University