This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Scientists develop thin film phototransistor for bioinspired visual adaptation
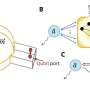
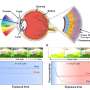
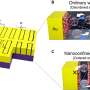
A research team led by Prof. Cao Hongtao at the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in cooperation with Prof. Zhang Haizhong's group from Fuzhou University, has developed a novel bioinspired vision sensor based on InP quantum dots (QDs)/oxide thin-film phototransistors.
The study was published in Advanced Functional Materials.
Artificial visual systems have broad application prospects in the security, medical care, service and other fields. However, massive and surging visual data pose a great challenge to the traditional artificial visual system, which is trapped by latency and energy consumption problems.
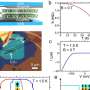
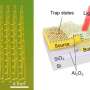
Adaptive phototransistors play a vital role in improving the efficiency of visual information processing. The researchers embed discrete InP QDs with strong visible-light absorbance within an InSnZnO thin film to construct a hybrid phototransistor, contributing to the efficient carrier transmission between the source and drain.
The excellent optoelectronic response capability of InP QDs and the superior electrical transport property of oxide semiconductors are perfectly combined in a single device.
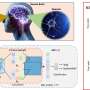
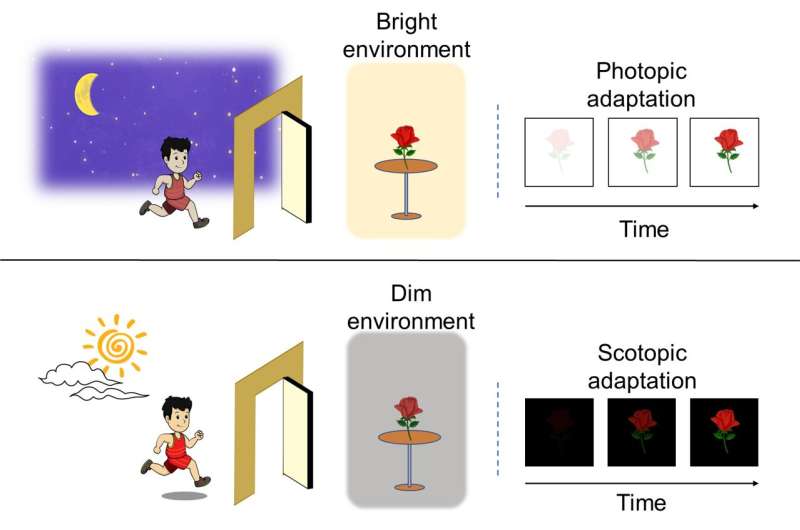
In addition, the developed bioinspired vision sensor based on the InP QDs/oxide thin-film phototransistor exhibits excellent gate controllability and visible light response capability, thus mimicking multiple functions of the human visual system and adapting to varying ambient light intensity.
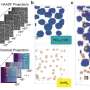
Moreover, the device achieved an impressive accuracy of more than 93% for handwritten pattern recognition, indicating its outstanding competence in image processing.
This study has provided an effective and facile way to fabricate high-performance phototransistors for bioinspired visual adaptation, and shed light on the further development of artificial vision systems.
More information: Zhixiang Gao et al, InP Quantum Dots Tailored Oxide Thin Film Phototransistor for Bioinspired Visual Adaptation, Advanced Functional Materials (2023). DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202305959
Journal information: Advanced Functional Materials
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences