This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Study suggests large mound structures on Kuiper belt object Arrokoth may have common origin
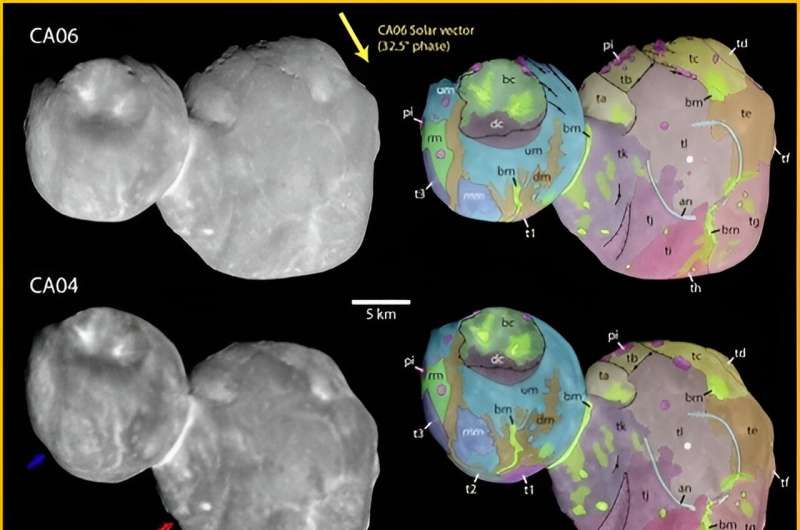
A new study led by Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) Planetary Scientist and Associate Vice President Dr. Alan Stern posits that the large, approximately 5-kilometer-long mounds that dominate the appearance of the larger lobe of the pristine Kuiper Belt object Arrokoth are similar enough to suggest a common origin.
The SwRI study suggests that these "building blocks" could guide further work on planetesimal formational models. Stern presented these findings this week at the American Astronomical Society's 55th Annual Division for Planetary Sciences (DPS) meeting in San Antonio. These results are now also published in the Planetary Science Journal.
NASA's New Horizons spacecraft made a close flyby of Arrokoth in 2019. From those data, Stern and his coauthors identified 12 mounds on Arrokoth's larger lobe, Wenu, which are almost the same shape, size, color and reflectivity. They also tentatively identified three more mounds on the object's smaller lobe, Weeyo.
"It's amazing to see this object so well preserved that its shape directly reveals these details of its assembly from a set of building blocks all very similar to one another," said Lowell Observatory's Dr. Will Grundy, co-investigator of the New Horizons mission. "Arrokoth almost looks like a raspberry, made of little sub-units."
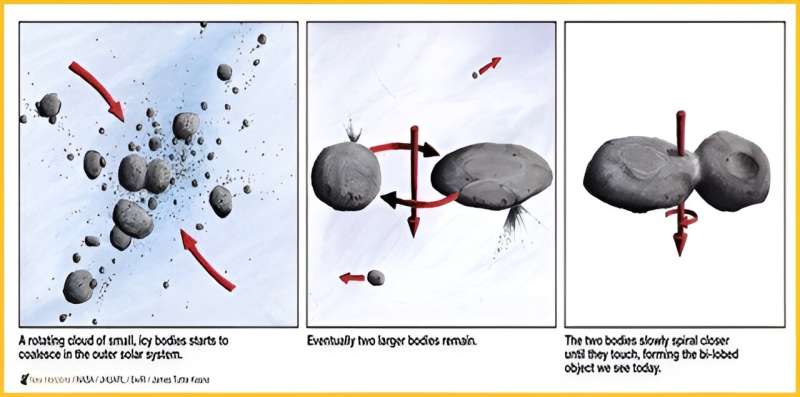
Arrokoth's geology supports the streaming instability model of planetesimal formation where collision speeds of just a few miles per hour allowed objects to gently accumulate to build Arrokoth in a local area of the solar nebula undergoing gravitational collapse.
"Similarities including in sizes and other properties of Arrokoth's mound structures suggest new insights into its formation," Stern, the Principal Investigator of the New Horizons mission, said. "If the mounds are indeed representative of the building blocks of ancient planetesimals like Arrokoth, then planetesimal formation models will need to explain the preferred size for these building blocks."
There is a good chance that some of the flyby targets for NASA's Lucy mission to Jupiter's Trojan asteroids and ESA's comet interceptor will be other pristine planetesimals, which could contribute to the understanding of accretion of planetesimals elsewhere in the ancient solar system and whether they differ from processes New Horizons found in the Kuiper Belt.
"It will be important to search for mound-like structures on the planetesimals these missions observe to see how common this phenomenon is, as a further guide to planetesimal formation theories," Stern said.
More information: S. A. Stern et al, The Properties and Origin of Kuiper Belt Object Arrokoth's Large Mounds, The Planetary Science Journal (2023). DOI: 10.3847/PSJ/acf317
Journal information: The Planetary Science Journal
Provided by Southwest Research Institute