This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Global study warns water security threatened by droughts and heat waves worldwide

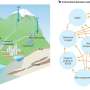
Increased demand for water due to global population growth, coupled with the increasing frequency of extreme weather events, endangers our water security. Nonetheless, little is known about the relationship of water use by sectors and the occurrence of drought-heat-wave events, particularly at the large scale.
To explore this issue, a group of researchers from the Department of Physical Geography from Utrecht University evaluated the responses of sectoral water use during droughts, heat waves and compound (combined) events at a global scale. The study, "Sectoral water use responses to droughts and heat waves: analyses from local to global scales for 1990-2019," published in Environmental Research Letters, shows that stronger sectoral water use responses are found for heat waves compared to impacts during droughts.
The research is the first global study quantifying sectoral water use responses under extremes droughts, heat waves and compound events. Sectoral water use responses are understood as how the water use practices of sectors (namely domestic, irrigation, thermoelectric energy, manufacturing and livestock) are affected by the occurrence of droughts, heat waves and compound events, which could lead them to increase or decrease their use of water or to show no particular reaction to these hydroclimatic extremes.
A large amount of data of sectoral water use at global, country and local scales during the last 30 years were analyzed. "We focused on the water used by various sectors, namely irrigation, livestock, domestic, energy and manufacturing, because we expected particular responses to the occurrence of different extreme events," says Gabriel Cardenas Belleza, Ph.D. candidate at Utrecht University and lead author of this publication.
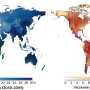
The analysis shows that extreme events over the last thirty years had substantial impacts on water use patterns, but these responses highly differ per sector and region across the world.
"Socio-economic factors and public water management plans strongly influence water use responses, and even more so during extreme events. For instance, while Western continental United States decreases its water use during extremes, the central US increases it," says Cardenas. In addition, the results reveal that the domestic and irrigation sectors, in general, have the highest priority for water use worldwide, however, stricter measures are taken in favor of the domestic sector during extremes.
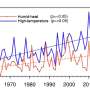
The analysis also shows that heat waves and compound drought-heat wave events overall have stronger impacts on water use in comparison to solely droughts. "Heat waves and compound events can lead to higher water use as a consequence of the temporary increase in water demand under high temperatures, which can still be satisfied due to the short duration of such extremes, compared to longer-lasting events like droughts," says Cardenas.
The results of the study demonstrate the urgency of collecting more water use data to better understand the implications of extreme events and climate change on different water use sectors and for improved assessments of future water scarcity.
"Our research provides a first step to evaluate multi-sectoral water use behavior during extremes. However, more local-scale information from data-scarce areas, like Africa and parts of Asia and South America, is needed to better understand sectoral water use behavior and improve water management strategies," Cardenas says.
More information: Gabriel A Cárdenas Belleza et al, Sectoral water use responses to droughts and heatwaves: analyses from local to global scales for 1990–2019, Environmental Research Letters (2023). DOI: 10.1088/1748-9326/acf82e
Journal information: Environmental Research Letters
Provided by Utrecht University