This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
El Niño's changing patterns: Human influence on natural variability
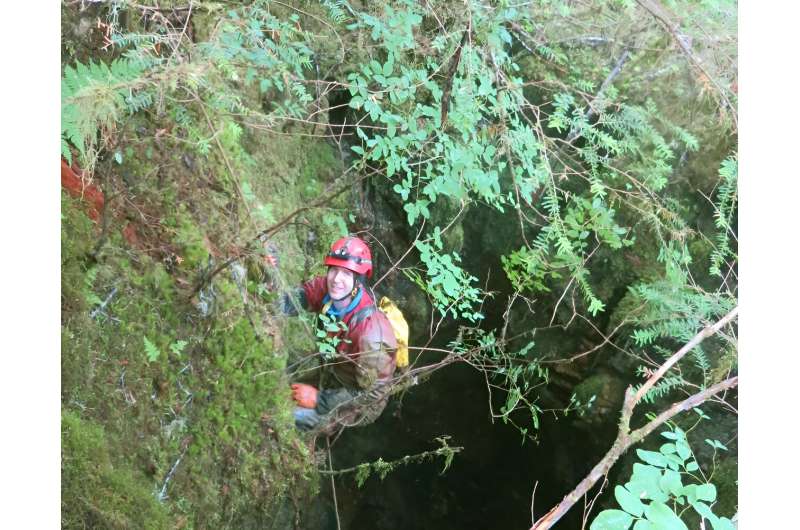

Two recent scientific studies led by Dr. Paul Wilcox from the Department of Geology at the University of Innsbruck provide new insights into Earth's climate dynamics, with a particular focus on the El Niño phenomenon. The results show how El Niño responds to natural factors over extended periods, while highlighting the increasing role of human activities in shaping this climatic phenomenon in the modern era.
El Niño signifies the warm phase of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO), one of the most crucial climate phenomena widely covered in the media due to its association with catastrophic weather events. It involves the warming of ocean waters in the eastern equatorial Pacific. Conversely, La Niña represents cooling in the eastern equatorial Pacific.
ENSO encompasses the cyclical variations in sea-surface temperatures, oscillating between warm El Niño and cold La Niña phases in the equatorial Pacific Ocean. In the face of ongoing environmental changes, understanding El Niño's response to both natural and human-induced factors becomes increasingly crucial for predicting and managing climate variability on a global scale.
Unraveling El Niño's response
In the journal Geophysical Research Letters, Paul Wilcox from the Quaternary Research Group led by Christoph Spötl sought to comprehend how El Niño responds to natural influences over extended periods. To achieve this, they analyzed cave deposits, known as speleothems, from southeastern Alaska. These speleothems preserved climate records spanning 3,500 years.
The results of the study suggest that the controlling processes of El Niño variability have changed since the 1970s. "Until about 50 years ago, changes in solar radiation played a significant role in shaping El Niño patterns. From the 1970s onwards, however, we see clear signals that can only be attributed to the consequences of man-made climate change," explains Wilcox.
New concept: The Walker switch
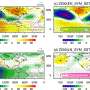
In the second study, published in The Innovation Geoscience, Wilcox turned his attention to examining climate shifts in southeastern Alaska over an extensive period of 13,500 years. The team utilized speleothems as invaluable records to investigate the cause of rapid, short-term climate changes that occurred during ice ages.
Despite its high northern latitude, southeastern Alaska displayed a climate pattern reminiscent of the equatorial Pacific during the end of the last ice age and the Holocene period. This contradicts the well-established "bipolar seesaw mechanism," which places the North Atlantic as the primary source for global climate variability. In lieu of this conventional mechanism, Wilcox and his team introduced the concept of the "Walker switch."
This mechanism, triggered by changes in solar radiation (insolation), instigates swift adjustments in sea-surface temperatures in the equatorial Pacific, subsequently influencing climate patterns in high northern latitudes, including Alaska and the North Atlantic. Wilcox elaborates, "The 'Walker switch' concept helps us better explain the complex interplay of factors that have shaped climate dynamics in these regions."
The results of both studies reveal a shift in El Niño patterns, where human activities are now overprinting natural factors to shape its behavior. "Climate change may have led to a climatic tipping point being crossed in the 1970s with the initiation of a more permanent El Niño pattern. Simultaneously, the introduction of the 'Walker switch' concept provides an alternative explanation for historical climate variations," explains Wilcox.
Triggered by alterations in solar radiation, the "Walker switch" influences climate patterns across the globe, including high northern latitudes. These findings underscore the dynamic complexity of Earth's climate system, emphasizing the need for ongoing research to deepen the understanding of climate processes.
More information: Paul S. Wilcox et al, Solar Forcing of ENSO on Century Timescales, Geophysical Research Letters (2023). DOI: 10.1029/2023GL105201
Paul S. Wilcox et al, A Walker switch mechanism driving millennial-scale climate variability, The Innovation Geoscience (2023). DOI: 10.59717/j.xinn-geo.2023.100026
Journal information: Geophysical Research Letters
Provided by University of Innsbruck