This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Anisotropic lattice induces high-Q chiroptical responses in surface lattice resonance metasurfaces
Chirality is an intrinsic property of an object that cannot coincide with its mirror image by translation or rotation. In order to realize strong chiral light-matter interactions which are usually weak in natural materials for practical applications, artificial sub-wavelength structures such as metamaterials, metasurfaces, and plasmonic nanostructures have attracted increasing attentions.
In many applications of chiral nanophotonics such as biochemical chiral sensing, chiral emission or lasing, and chiral nonlinear responses, strong optical chirality simultaneously with high Q factors are highly desirable but challenging to achieve.
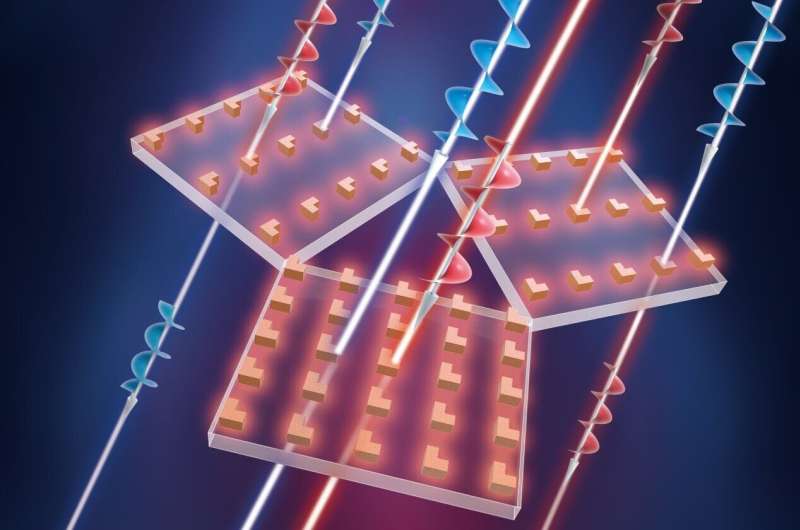
In a study published in Laser & Photonics Reviews, a research group led by Dr. Li Guangyuan from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences experimentally demonstrated that anisotropic lattice could induce strong chirality in metasurfaces.
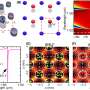
In a silicon metasurface, planar chiral mode with circular dichroism 0.37 and Q factor 1220 was experimentally observed under normal incidence by breaking the periodic symmetry. The measured Q factor was several times of that of planar bound states continuum (BIC) metasurfaces.
Although chiral BIC is a promising way to improve the Q factor, inherent contradictory dependencies on asymmetry parameter of high Q factor and strong chirality, restricts further improvements and applications.
The research group found that surface lattice resonances (SLRs) is an effective way to compromise the conflict. SLRs, originating from coherent coupling between localized resonances and the Rayleigh anomaly, possess great spectral tunability and ability of suppressing the absorption and radiation losses.
By merely breaking the periodic symmetry in x- and y-direction while keeping the mirror symmetry of the nanostructures, strong planar chirality can be produced under normal incidence without deteriorating the Q factor.
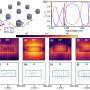
The maximum simulated CD reaches 0.86 while the Q factor can be as high as 1700. The sign of CD value is inversible by setting the lattice period in the x direction larger or smaller than that in the y direction. Additionally, extrinsic chirality is also observed under oblique incidence, and large CD of 0.7 and simultaneously high Q factor of 872 can be numerically obtained.
"We expect that this high-Q and strong chiroptical metasurface will find applications in chiral sensing and wavefront modulations," said Dr. Li.
More information: Xiaoqing Luo et al, High‐Q and Strong Chiroptical Responses in Planar Metasurfaces Empowered by Mie Surface Lattice Resonances, Laser & Photonics Reviews (2023). DOI: 10.1002/lpor.202300186
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences