This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Researchers unveil new flexible adhesive with exceptional recovery and adhesion properties for electronic devices
The rapid advancements in flexible electronic technology have led to the emergence of innovative devices such as foldable displays, wearables, e-skin, and medical devices. These breakthroughs have created a growing demand for flexible adhesives that can quickly recover their shape while effectively connecting various components in these devices.
However, conventional pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSAs) often face challenges in achieving a balance between recovery capabilities and adhesive strength. In an extraordinary study conducted at UNIST, researchers have successfully synthesized new types of urethane-based crosslinkers that address this critical challenge.
Led by Professor Dong Woog Lee from the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST, the research team developed novel crosslinkers utilizing m-xylylene diisocyanate (XDI) or 1,3-bis(isocyanatomethyl)cyclohexane (H6XDI) as hard segments along with poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) groups serving as soft segments. By incorporating these newly synthesized materials into pressure-sensitive adhesives, they achieved significantly improved recoverability compared to traditional methods.
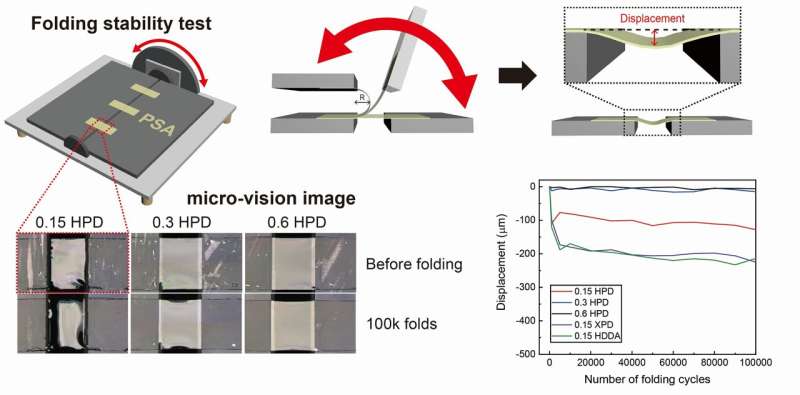
The PSA formulated with H6XDI-PEG diacrylate (HPD) demonstrated exceptional recovery properties while maintaining high adhesion strength (~25.5 N 25 mm−1). Through extensive folding tests totaling 100k folds and multi-directional stretching tests spanning 10k cycles, the PSA crosslinked with HPD exhibited remarkable stability under repeated deformation—showcasing its potential for applications requiring both flexibility and recoverability.
Furthermore, even after subjecting the adhesive to strains up to 20%, it displayed high optical transmittance (>90%), making it suitable for fields such as foldable displays that demand not only flexibility but also optical clarity.
"This breakthrough in adhesive technology offers promising possibilities for electronic products that require both high flexibility and rapid recovery characteristics," said Professor Lee. "Our research addresses the long-standing challenge of balancing adhesion strength and resilience, opening up new avenues for the development of flexible electronic devices."
Hyunok Park, a researcher involved in the study, emphasized the significance of this research by stating, "The introduction of this new crosslinking structure has led to an adhesive with exceptional adhesion and recovery properties. We believe it will drive future advancements in adhesive research while contributing to further developments in flexible electronics."
The study findings have been published in Advanced Functional Materials.
More information: Hyunok Park et al, Tailoring Pressure Sensitive Adhesives with H6XDI‐PEG Diacrylate for Strong Adhesive Strength and Rapid Strain Recovery, Advanced Functional Materials (2023). DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202305750
Journal information: Advanced Functional Materials