This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Exploring just how extreme future storms could get
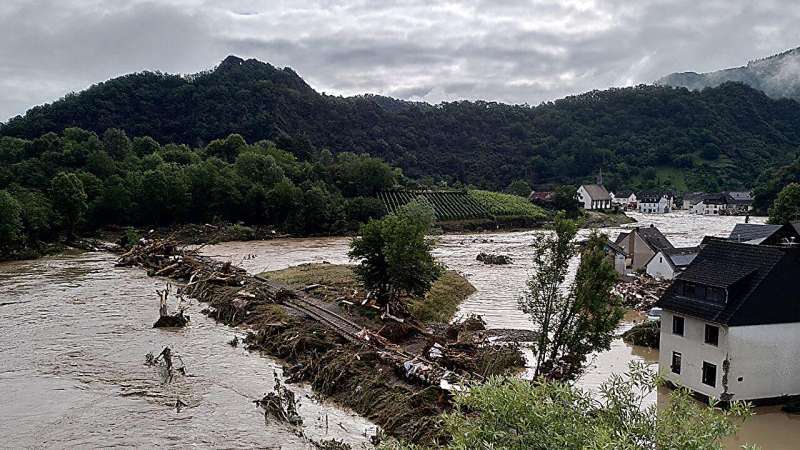

Storms that drop exceptionally high volumes of precipitation often cause flooding and otherwise imperil human safety, infrastructure and ecosystems. As climate change progresses, such extreme events are likely to become even more intense and more frequent in many regions around the world.
Efforts to prepare for future extreme events benefit from accurate estimates of just how intense these events might be. However, because the most extreme events are rare, available historical records are often too short to contribute to reliable estimates.
Claudia Gessner and colleagues have demonstrated a novel way to combine storm simulations with statistical approaches to better estimate how extreme future precipitation events could become. Focusing on central Europe and the colder months of October–April, the researchers first applied a statistical approach to evaluate the plausibility of future extreme events predicted from real-world historical data and from simulations generated using the Community Earth System Model Version 2.
The resulting analysis suggested that precipitation events much more intense than previously have been recorded will be possible in the near future in the region. The study is published in the journal Earth's Future.
However, those statistical estimates came with a high degree of uncertainty and did not address the physical mechanisms behind future extreme events. So the researchers next applied a strategy known as ensemble boosting, which involves generating many alternative simulations of how a past, real-world extreme precipitation event may have unfolded over time, depending on very small perturbations in humidity several days prior to the event.
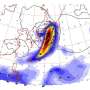
This approach produced estimates indicating that near-future extreme events might result in precipitation volumes that are 30%–40% higher than those seen in past events. The researchers note that even higher precipitation magnitudes cannot be ruled out. Further, their analysis suggested that some of the most extreme winter precipitation events in Europe can be linked to patterns of atmospheric pressure at sea level typically associated with atmospheric rivers—bands of intense moisture transport through the atmosphere.
The researchers say the findings together suggest that the ensemble boosting and statistical approaches can complement each other well in efforts to estimate the intensity of future extreme events, providing a way to "stress test" the resilience of infrastructure and ecosystems in the face of such events.
More information: C. Gessner et al, Developing Low‐Likelihood Climate Storylines for Extreme Precipitation Over Central Europe, Earth's Future (2023). DOI: 10.1029/2023EF003628
Journal information: Earth's Future
Provided by Eos
This story is republished courtesy of Eos, hosted by the American Geophysical Union. Read the original story here.