This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Study: Social justice for traditional knowledge holders will help conserve Europe's nature
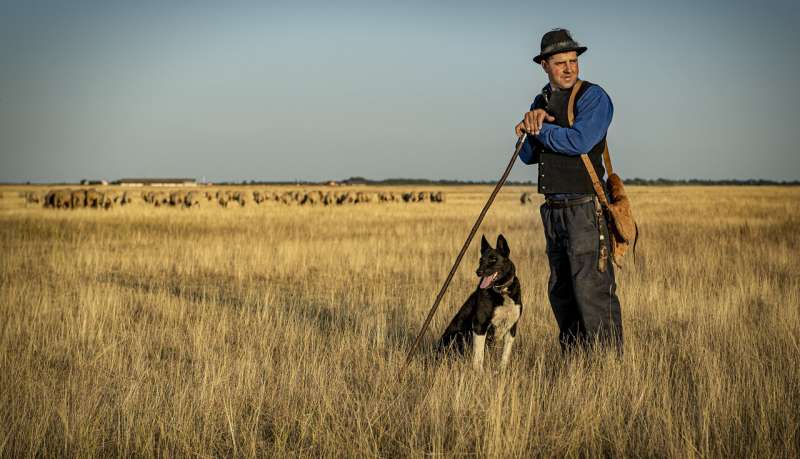

It is well known that biodiversity of cultural landscapes is threatened by land abandonment and agricultural intensification. Traditional, low chemical and machinery input management systems have long been acknowledged for their diverse benefits to maintain and enhance biodiversity; however, the recognition of traditional knowledge, on which these traditional management practices are based, started only relatively recently.
The recognition of traditional knowledge holders themselves is an even more recent phenomenon. A recently published paper aims to help increase recognition and respect towards these people, and through this, also support the conservation and restoration of species-rich cultural landscapes across Europe.
The findings are published in the journal Biological Conservation.
"Traditional knowledge holders are small-scale, traditional farmers and herders, but also many forest users, hunters, fishers and foragers that know, manage and steward their surrounding environment based predominantly on traditional knowledge and practices," explains Zsolt Molnár, the lead author of the study. "Across Europe, we've seen that the lack of recognition towards these people may easily lead to social injustices."
The authors of the study summarized their experience on social injustices and their consequences to conservation. They found social injustices spanning from disrespect by the society and misrepresentation in public mindscapes, invisibility in the media, misunderstanding by scientists and other stakeholders, economic and political vulnerability caused by inappropriate regulations and unfair market competitions, unethical collaborations, rights violations, uncontextualized education to lack of inclusivity in conservation planning and management.

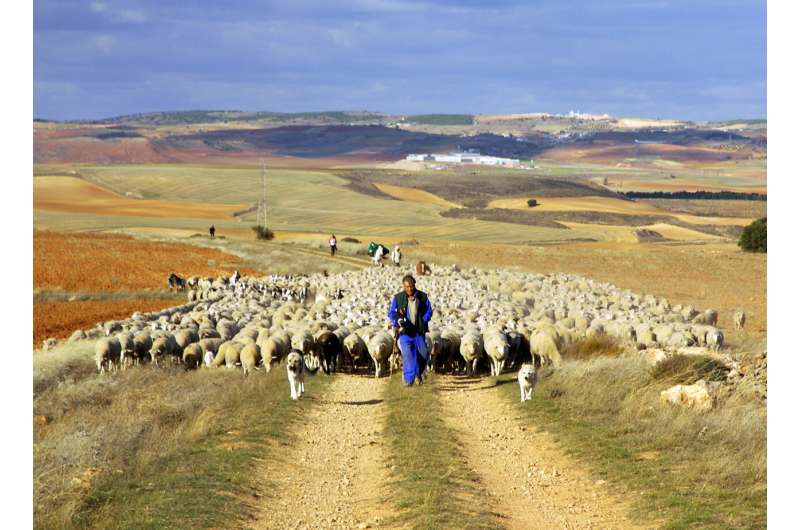
Let's look at some concrete examples. Traditional knowledge-based farmers mostly manage smaller farms, while larger farms benefit disproportionately from agricultural subsidies. Moreover, former have bureaucratic and structural disadvantages when applying for subsidies, resulting in billions of euros being misspent from a social and conservation perspective.
Hungarian herders have a highly respected heritage of folk dances, clothes and handicrafts, but no meaningful formal participation in protected area management, even where conservation grazing is vital. The continuity of Spanish transhuman pastoralism depends partly on its related knowledge, which is linked to the maintenance of transhumance of food.
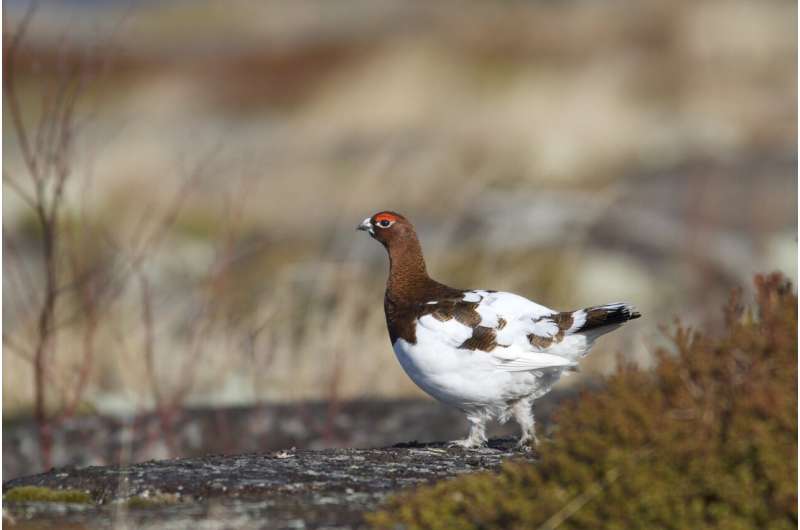
This practice is threatened by legal disadvantages of long-distance mobility between different governing entities. The traditional Sámi calendar of ptarmigan hunting conflicts with the imposition of national hunting season regulations in northern Fennoscandia. Hunting is allowed to start earlier, which results in substantial extra disturbance towards the birds by non-local hunters.
The European Union and its member states have diverse responsibilities under international instruments to ensure that traditional knowledge holders can continue their ways of life (if they wish to do so), that is so often beneficial for conservation in cultural landscapes.

The scientific literature reviewed consistently shows that resolving these social injustices would result in simultaneous benefits both for people and nature. The urgency of resolving these social injustices becomes even more apparent in the wake of the recent adoption of the EU Nature Restoration Law. Traditional knowledge holders can and should play a prominent role in the implementation of this ambitious program.
"Conservation rangers wouldn't talk to us 20 years ago. They criticized us without asking us anything. Now they stop and we can talk about pasture management. We agree on about 90% of things. The difference between them and me is that for the rangers, it's all about the plants [protected plant species], but for me it's all about the animals [livestock]," says László Sáfián, a traditional shepherd from Hungary, one of authors of the study. "If you know in which season and how a heavily degraded weedy pasture needs to be grazed, by cattle or sheep, under the supervision of a good herder, you can restore it much easier than with a machine, and for lower costs," he added.
Indeed, well-established evidence shows that mutual understanding and respectful collaboration between traditional knowledge holders and conservationists can lead to better compromises in conservation management and regulations. Improving recognition also underpins the success of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework that aims to halt and reverse further loss of biodiversity. Fortunately, there is an increasing number of good examples of how social injustices are being actively resolved and/or prevented in Europe.
The ongoing functioning of low-external-input agricultural systems is vital for European food resilience in an era of pandemics, energy crises and as a response to mitigate the impacts of Russia's invasion of Ukraine. It is not enough to save traditions for folklore stage performances and skanzens, the only possible way to keep alive traditional knowledge and practices is to maintain their adaptive character.
Sustaining traditional knowledge requires safeguarding not only the knowledge itself, but most importantly, the social and ecological spaces where this knowledge is enacted, transmitted and shared.
Not only rare and threatened animal and plant species but the vulnerable and often-forgotten traditional knowledge holders of Europe call for urgent action, including the resolution of the many social injustices they continue to face while struggling in making a living in some of Europe's most biodiverse landscapes.
More information: Zsolt Molnár et al, Social justice for traditional knowledge holders will help conserve Europe's nature, Biological Conservation (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.biocon.2023.110190
Journal information: Biological Conservation
Provided by Ökológiai Kutatóközpont