This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Metal organic framework nanosheets employed as ion carriers for self-optimized zinc anode

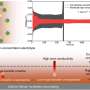
Aqueous rechargeable zinc ion batteries are promising components for electric grid storage due to their low cost and intrinsic safety. However, their practical implementation is hindered by poor reversibility of the zinc anode, primarily caused by the chaotic Zn deposition present as dendrite and side reactions.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. Yang Weishen and Dr. Zhu Kaiyue from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has proposed a strategy using "ion carriers" by importing macromolecular Zn2+ carriers with a large mass-to-charge ratio to decouple the ion flux from the inhomogeneous electric field and substrate. This method provides an efficient pathway to overcome the dendrite and side reaction problems.
This study was published in Energy & Environmental Science on Aug. 18.
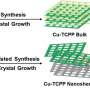
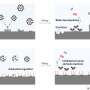
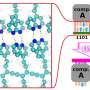
The researchers found that metal organic framework (MOF) nanosheets featuring migration capability under electric field due to their one-dimensional channel structure and preferential Zn2+ adsorption, as well as unique reductive chemistry due to the weak coordination between ligands and zinc ions, enables them to serve as dynamic Zn2+ ion carriers.
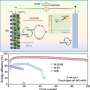
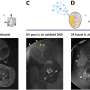
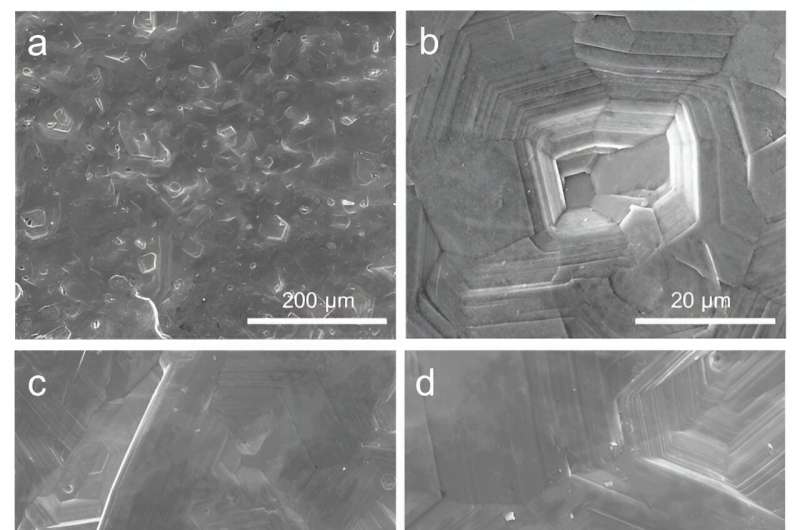
The dynamic MOF nanosheets could continually optimize zinc anode during cycling. Specifically, the zinc electrode was gradually reconstructed towards a horizontally aligned lamellae-like morphology and enhanced (002) texture, showing a relative texture coefficient of a 96.9 (maximum value of 100). This optimization on the morphology and texture could be attributed to the horizontal alignment of Zn2+ ions by the constraints of MOF nanosheets.
Additionally, the presence of MOF ligands contributed to the elimination of undesirable Zn4SO4(OH)6·4H2O byproducts. These byproducts were spontaneously converted into useful MOF nanosheets through unique properties of ligands. Consequently, Zn||Zn symmetric cells and Zn||(NH4)2V10O25·8H2O full cells employing MOF nanosheets in electrolytes exhibited outstanding cycling performance at both low and high rates.
"The versatility of the 'ion carrier' strategy holds promise for potential expansion into achieving highly reversible cycling in other rechargeable metal cells, owing to its broad applicability to various ligands, substrates and electrolytes," said Prof. Yang.
More information: Hanmiao Yang et al, MOF Nanosheets as Ion Carriers for Self-Optimized Zinc Anode, Energy & Environmental Science (2023). DOI: 10.1039/D3EE01747H
Journal information: Energy & Environmental Science
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences