This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Artificial DNA structures fitted with antibodies may instruct the immune system to target cancerous cells
A new study highlights the potential of artificial DNA structures that, when fitted with antibodies, instruct the immune system to specifically target cancerous cells.
Immunotherapy is viewed as an exceptionally promising weapon in the fight against cancer. In essence, the aim is to activate the body's immune system in such a way that it identifies and destroys malignant cells. However, the destruction must be as effective and specific as possible, to avoid damaging healthy cells.
A team of researchers from LMU, the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and Helmholtz Munich have now published a new study in Nature Nanotechnology in which they present a promising method for developing user-defined agents that can do precisely that.
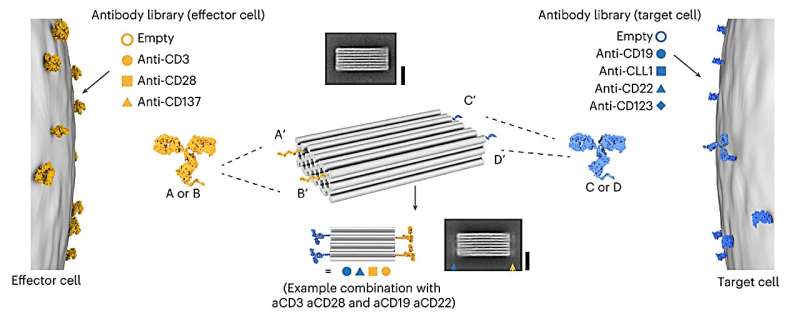
"The centerpiece is a tiny chassis of folded DNA strands that can be specifically fitted with any antibodies," explains Professor Sebastian Kobold, one of the main authors. At Munich University Hospital, his team has investigated the impact of the new substrates both in vitro and in vivo.
Using DNA origami to recruit T-cells
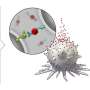
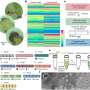
This novel class of agents, coined "programmable T-cell engagers" (PTEs) are created with DNA origami, a nanotechnology in which self-folding DNA strands assemble themselves into a structure simulated in advance on a computer. Their design allows different antibodies to be attached in four positions.
Antibodies that specifically bind to certain tumor cells are added on the one side, while antibodies that are recognized by the immune system's T-cells are mounted on the other. T-cells then destroy the marked cells. "This approach permits us to produce all kinds of different PTEs and adapt them for optimized effects," says Dr. Adrian Gottschlich, one of the study's lead authors.
"Infinite combinations are in theory possible, making PTE a highly promising platform for treating cancer." The scientists produced 105 different combinations of antibodies for the study, testing them in vitro to see how specifically they attached themselves to the target cells and how successful they were at recruiting T-cells. The combinations could be generated in a modular way and without the previous very time-consuming optimization of the antibodies.
The team was able to prove that more than 90% of the cancer cells had been destroyed after 24 hours. To find out whether this also worked in living organisms, Professor Kobold and his colleagues examined whether PTEs also recognize and induce the destruction of cancer cells in tumor-bearing organisms. "We were able to prove that our PTEs made from DNA origami structures also work in vivo," Gottschlich says.
Versatile and user-defined
Gottschlich explains that, thanks to the possibility of mounting different antibodies at the same time, tumor cells can be targeted much more precisely. It is also easier to control activation of the immune system. This increases the prospects of successfully treating cancer by distinguishing more accurately between diseased and healthy cells and thus minimizing side effects. In light of the DNA origami technologies' modular nature, adaptability and high degree of addressability, the researchers expect that a broad spectrum of complex and even logic-controlled immunotherapy platforms can be developed.
TUM scientists Dr. Klaus Wagenbauer, Dr. Benjamin Kick, Dr. Jonas Funke and Professor Hendrik Dietz all number among the founders of Plectonic Biotech GmbH that wants to further develop and market the technology underpinning PTEs. Sebastian Kobold says, "We believe that our findings will permit the clinical testing of DNA nanotechnologies and demonstrate the potential of biomolecular, DNA-origami-based engineering strategies for medical applications."
More information: Klaus F. Wagenbauer et al, Programmable multispecific DNA-origami-based T-cell engagers, Nature Nanotechnology (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41565-023-01471-7
Journal information: Nature Nanotechnology
Provided by Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich