This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Decrypting lunar craters quickly and easily
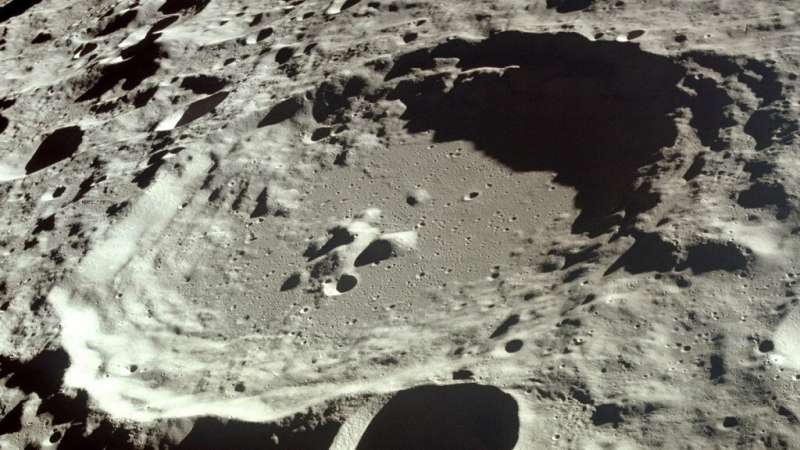

The surface of the moon tells the story of the inner solar system. Every meteorite that hits leaves its mark, and together those craters hold a record of the events that have occurred on and around the moon over the past 4 billion years.
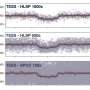
But the record can be hard to read. The ages and spatial densities of craters are critical metrics for decoding the moon's impact history, but analyzing these properties can be time-consuming and sometimes requires bringing samples back to Earth.
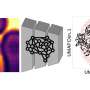
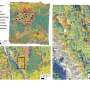
J. H. Fairweather and colleagues show, in an article published in Earth and Space Science, that machine learning could be a quick and easy way to improve our understanding of lunar craters. By training an algorithm on more than 50,000 images of previously characterized craters, the researchers were able to estimate the ages and densities of many more of the moon's multitudinous marks.
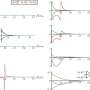
At first, the machine learning algorithm's estimates differed substantially from those other researchers had derived by hand. But with a bit of manual curation, Fairweather and his colleagues were able to bring their automated estimates of crater age and density in line with previous estimates.
Lighting conditions presented one issue. If craters were partially shaded by rocks or located on unevenly lit slopes, the algorithm had trouble analyzing them accurately. Excluding such craters improved the accuracy. The presence of rocks or buried craters also led the algorithm to overestimate crater ages by 10%–45%, but it could determine very accurate ages for young lunar surfaces and impact craters once rocks, buried craters, and other unwanted objects were removed from the images.
The researchers caution that although machine learning can provide a wealth of information about the moon's surface, the algorithms still require careful oversight.
More information: J. H. Fairweather et al, Lunar Surface Model Age Derivation: Comparisons Between Automatic and Human Crater Counting Using LRO‐NAC and Kaguya TC Images, Earth and Space Science (2023). DOI: 10.1029/2023EA002865
Journal information: Earth and Space Science
Provided by Eos
This story is republished courtesy of Eos, hosted by the American Geophysical Union. Read the original story here.