This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Astronomers find high-frequency magnetic waves may play essential role in coronal heating
A joint scientific team led by the Royal Observatory of Belgium (ROB) and the KU Leuven has found that high-frequency magnetic waves could play an essential role in keeping the sun's atmosphere at millions of degrees. This finding sheds a new light on the most intriguing solar mystery: what makes the sun's atmosphere hotter than its surface?
One of the long-standing astrophysical puzzles is exactly this coronal heating problem. From a young age, we are taught that temperature decreases as you move away from a heat source, but this is not true for the sun. The sun's only heat source resides in its core. Yet the corona, the outermost layer of the solar atmosphere, is about 200 times hotter than the photosphere, the sun's surface.
Prof. Tom Van Doorsselaere at KU Leuven says, "Over the past 80 years, astrophysicists have tried to solve this problem and now more and more evidence is emerging that the corona can be heated by magnetic waves."
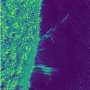
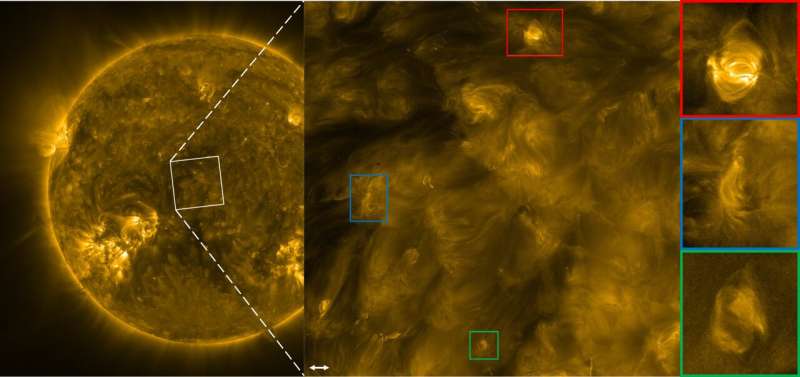
This new insight has been developed from observations by the Extreme Ultraviolet Imager (EUI) telescope onboard Solar Orbiter, a spacecraft of the European Space Agency ESA, that is currently observing the sun from behind.
The EUI telescope, operated by ROB, produces images of the solar corona with unprecedented resolution. Its observations reveal fast oscillations in the smallest magnetic structures of the solar corona, and the energy of these high-frequency waves contributes to the heating of the solar atmosphere. The findings are published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
The main question the scientists were asking was whether the energy originating from these new, fast oscillations outweighed the energy coming from similar, but slower oscillations that were already known.
The scientific team performed a meta-analysis, which is a statistical method of using multiple scientific studies to derive common unknown truths. Dr. Daye Lim, lead author, concluded that high-frequency waves give a more significant contribution to the total heating generated by waves than low-frequency waves.
Dr. David Berghmans, the principal investigator of EUI, says, "Since her results indicated a key role for fast oscillations in coronal heating, we will devote much of our attention to the challenge of discovering higher-frequency magnetic waves with EUI."
More information: Daye Lim et al, The Role of High-frequency Transverse Oscillations in Coronal Heating, The Astrophysical Journal Letters (2023). DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/ace423
Journal information: Astrophysical Journal Letters
Provided by Royal Observatory of Belgium