This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Study proposes achromatic metalens with varifocal performance
Metalenses, comprising one of the most prominent applications of metasurfaces, demonstrate promising abilities to replace traditional lenses. By manipulating the phase distribution of metalenses composed of appropriately arranged meta-atoms, the wavefront of incidence can be arbitrarily controlled to achieve desired purposes.
Broadband achromatic metalenses (BAMs) that correct chromatic aberration in broadband applications have found practical applications. However, existing BAMs are limited to a single functionality, which impedes potential applications after fabrication. Producing continuously varifocal metalenses for broadband achromatic focusing is still a challenge.
To overcome this challenge, a research team led by Prof. Dr. Fan Wenhui from Xi'an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics (XIOPM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed a metalens for designing tunable BAMs, a continuously varifocal and broadband achromatic metalens (CVBAM). The study was published in the Journal of Science: Advanced Materials and Devices.
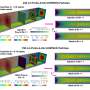
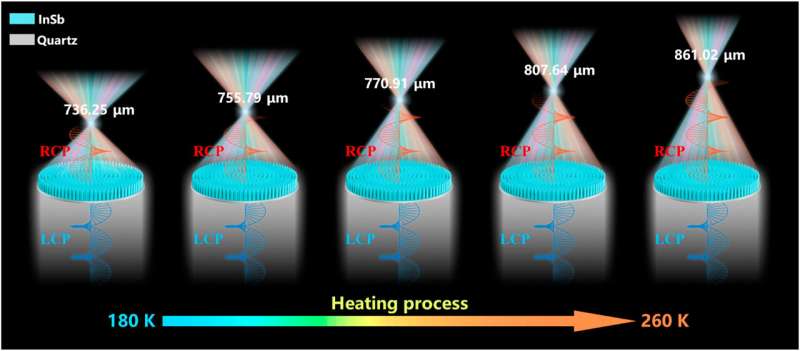
The researchers selected the semiconductor material indium antimonide (InSb) with tunable responses to design meta-atoms for accomplishing phase compensation required by CVBAM with the operation frequency range of 1.8 to 2.2 THz.
The CVBAM was designed to converge the focal spots to a preset spatial location over the operation frequency range. By varying the external temperature, the focal length of the CVBAM can be dynamically tuned from 736.25 μm to 861.02 μm, while the achromatic focusing can be maintained, as well.
The proposed metalens can significantly enrich the capabilities and potential applications of current meta-devices, which may facilitate the development of THz near-field imaging and spectroscopy systems.
More information: Xiao-Qiang Jiang et al, Continuously varifocal metalens for broadband achromatic focusing of terahertz waves, Journal of Science: Advanced Materials and Devices (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.jsamd.2023.100560
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences