This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Researchers uncover a novel preference structure to explain the aesthetics behind our everyday choice of clothing
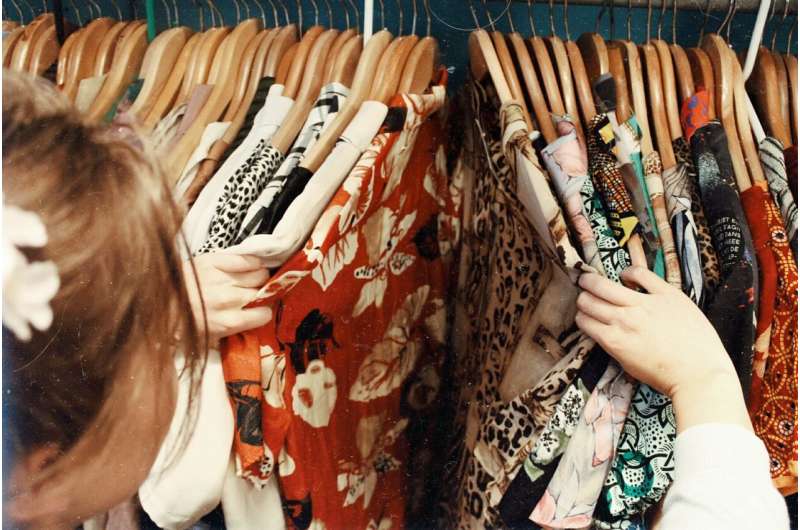

While each person gets dressed at least 29,000 times in the course of their lives, empirical science has paid little attention to why we select the everyday clothes that help mold our image.
In one of the first studies of its type, researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and London College of Fashion (LCF), University of the Arts (UAL), have explored the aesthetics of fashion to uncover preferences like style (shape and cut), color (hue, brightness and saturation), and personality differences that motivate people to buy and wear clothing for work, leisure, and more formal occasions. The study was published in Empirical Studies of the Arts.
"Preference has been studied for ages across a wide range of art and aesthetic domains, from paintings to music, but almost never in the context of fashion, which is unquestionably a social experience and mode of self-expression," says co-author Nancy Etcoff, Ph.D., director of the Program in Aesthetics and Well Being at MGH and Harvard Medical School.
"We asked in our research whether fashion aesthetics could be studied empirically, and not only discovered it can, but that it opens the door to better understanding factors that guide people in their everyday clothing preferences. This knowledge is valuable to designers and marketers of clothing as well as to consumers themselves by putting them in better touch with their aesthetic tastes and sensibilities."
From the research team's online survey of 307 females and 191 males in the United Kingdom, a novel preference structure emerged across four types of clothing styles: essential, comfortable, feminine, and trendy.
Further analysis found that preferences across each of these styles were associated with the color preferences and the self-reported traits (e.g., personality) of study participants.
More specifically, prominent color preferences for those who liked and owned feminine clothing (e.g., dresses and skirts) consisted of lilac, violet, pink, turquoise, and dark red, and for people who wore essential clothing (e.g., shirts and jackets) dark blue, blue and brown were the favored colors.
In addition, the study showed that people with a propensity for feminine clothing displayed high levels of fashion leadership, an appreciation for the importance of dressing well and, on the behavioral scale, tended to show more compassion.
On the other hand, individuals who liked and owned essential clothing tended to be sociable, exhibited higher energy, and were emotionally stable.
Wearers of comfortable clothes (e.g., hoodies, sweatpants, tracksuits) were also identified with fashion leadership and interest, while those whose taste ran to trendy articles (e.g., dungarees, polo shirts, boiler suits) tended to be young and had an appreciation for the visual arts.
"The more one knows about and appreciates the aesthetics of fashion, the more attention they will pay to what they're wearing and what excites them when viewing clothing," says lead author Young-Jin Hur, Ph.D., with London College of Fashion/UAL.
"Because aesthetic experiences seem linked with well-being, our findings may provide an important commentary on how this could impact the wearer's self-confidence."
Adds senior author Emmanuel Sirimal Silva, Ph.D., with LCF/UAL, "Our findings underscore that clothing preferences are closely linked to fashion experience and to the individual's identity."
Etcoff, who authored the book "Survival of the Prettiest: The Science of Beauty," believes her team's latest research opens the door to an exciting new body of discovery around fashion behaviors and preferences, such as clothing textures and patterns as well as the impulses that drive constant change in the multi-billion-dollar clothing field.
"Each of us spends a lot of money on clothing," she observes, "and what we're attempting to do through our work is more fully inform the decisions we make to look better and to complement our personalities."
More information: Young-Jin Hur et al, Can Fashion Aesthetics be Studied Empirically? The Preference Structure of Everyday Clothing Choices, Empirical Studies of the Arts (2022). DOI: 10.1177/02762374221143727
Provided by Massachusetts General Hospital