This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Who are the first ancestors of present-day fish?

What is the origin of the ancestors of present-day fish? What species evolved from them? A 50-year-old scientific controversy revolved around the question of which group, the "bony-tongues" or the "eels", was the oldest.
A study by INRAE, the CNRS, the Pasteur Institute, Inserm and the Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle, has just put an end to the debate by showing through genomic analysis that these fishes are in fact one and the same group, given the rather peculiar name of "Eloposteoglossocephala." These results, published in Science, shed new light on the evolutionary history of fish.
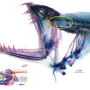
Understanding the evolutionary history of species through their relatedness is an essential issue and regularly the subject of scientific controversy. One of them concerns the position, in the tree of life, of the three oldest groups of teleost fishes, which appeared towards the end of the Jurassic period (from 201.3 to 145 million years ago) and which include most of our present-day fishes.
These three groups consist of the "bony-tongues," the "eels" and a group that unites all other species of teleost fishes. Early classifications in the 1970s, based solely on anatomical criteria, had classified the "bony-tongues" as the oldest group. Modern classification approaches, however, based on the use of DNA sequences to reconstruct the evolutionary history of life, placed the "eels" as the oldest group. Ever since, controversy has ensued.
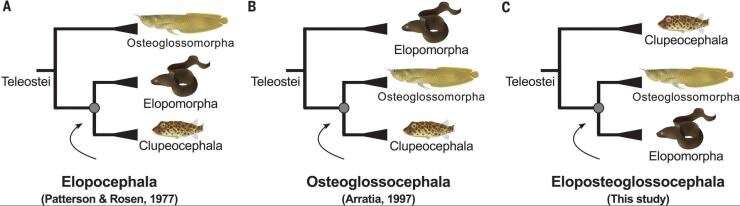
What if both hypotheses were wrong?
To investigate this question, scientists sequenced the genomes of several species in the "eel" group, including the European eel and the giant moray eel. They analyzed the DNA sequences to gain insight into the structure and organization of the genes within the genome. They were thus able to reconstruct, in a very reliable way, the relationships between the different teleost fishes, which led to an end of the controversy without winners or losers: neither hypothesis was valid.
Surprisingly, scientists have discovered that the two groups of "eels" and "bony-tongues" are in fact one and the same in terms of evolutionary history. The researchers have named this group "Eloposteoglossocephala." These results put an end to more than fifty years of controversy about the evolutionary history of the main branches of the teleost fish tree of life. They shed new light on the evolutionary history of fishes and the understanding of evolutionary processes.
More information: Elise Parey et al, Genome structures resolve the early diversification of teleost fishes, Science (2023). DOI: 10.1126/science.abq4257. www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abq4257
Journal information: Science
Provided by INRAE