This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Next-generation, light-activated nanotech for antibiotic-resistant superbugs
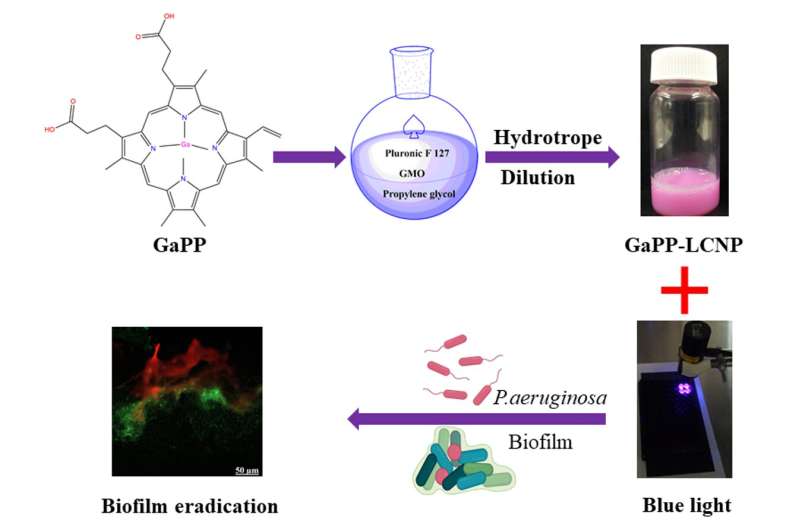
It's "lights out" for antibiotic-resistant superbugs as next-generation light-activated nanotech proves it can eradicate some of the most notorious and potentially deadly bacteria in the world.
Developed by the University of South Australia and published in Pharmaceutics, the new light therapy can eliminate antibiotic-resistant superbugs golden staph and Pseudomonas aeruginosa by 500,000-fold and 100,000-fold respectively.
Golden staph (staphylococcus aureus) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa are among the most deadly superbugs in the world. Globally, about 1.27 million people die as a result of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Lead researcher, UniSA's Dr. Muhammed Awad, says the new light therapy will be a game-changer for millions of people worldwide.
"Golden staph and Pseudomonas aeruginosa are both highly transmissible bacteria, commonly found on people's skin. But if they get into the blood, they can lead to sepsis or even death," Dr. Awad says.
"Patients in hospitals—particularly those with wounds or catheters, or those on ventilators—have a higher risk of getting these bacteria, and while antibiotics may help, their extensive use has led to waves of microbial resistance, often making them ineffective.
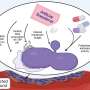
"Our photodynamic technology works differently, harnessing the energy of light to generate highly reactive oxygen molecules that eradicate microbial cells and kill deadly bacteria, without harming human cells."
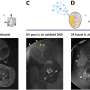
The researchers tested the antimicrobial photodynamic therapy on recalcitrant bacterial infections caused by antibiotic resistant strains of golden staph and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Senior researcher, UniSA's Professor Clive Prestidge, says that the technology has some key advantages over conventional antibiotics and other light therapies.
"The new therapy is created in an oil that that is painted on a wound as a lotion. When laser light is applied to the lotion, it creates reactive oxygen species which act as an alternative to conventional antibiotics," Prof. Prestidge says.
"Current photoactive compounds also suffer from poor water-solubility which mean that they have limited clinical application.
"Our approach uses food grade lipids to construct nanocarriers for the photoactive compound which improves its solubility and antibacterial efficiency far beyond that of an unformulated compound.
"These molecules target multiple bacterial cells at once, preventing bacteria from adapting and becoming resistant. So, it's a far more effective and robust treatment.
"Importantly, the human skin cells involved in the wound healing process showed enhanced viability, while the antibiotic resistant bacteria were entirely eradicated."
The consequences of not managing superbugs are high. Already, antibiotic resistant microbials cost millions of lives and trillions of dollars to the global economy each year.
"This technology is very promising and is gaining the attention of scientists worldwide," Prof. Prestidge says.
"The next step is to commence clinical trials and develop this technology further to be available in clinics. With the support of funding bodies, we hope that Australians will have access to this technology as soon as possible."
More information: Muhammed Awad et al, Gallium Protoporphyrin Liquid Crystalline Lipid Nanoparticles: A Third-Generation Photosensitizer against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms, Pharmaceutics (2022). DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14102124
Muhammed Awad et al, Liquid crystalline lipid nanoparticle promotes the photodynamic activity of gallium protoporphyrin against S. aureus biofilms, Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2022.112474
Muhammed Awad et al, Nanomaterials enabling clinical translation of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy, Journal of Controlled Release (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.04.035
Journal information: Journal of Controlled Release
Provided by University of South Australia