This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Explanation found for puzzling observation of Shiba states in superconductors

The origin of a mysterious experimental observation in a superconductor with a magnetic impurity sitting on top of it has been revealed in a theoretical study by a RIKEN researcher and a collaborator. This could help realize a robust quantum state residing in a superconductor that may find application in quantum computers.
Superconductors conduct electricity without any resistance because electrons in them form pairs that have an energy gap. But placing a magnetic atom on top of a superconductor creates a new state in this energy gap as a result of the atom's magnetism interacting with the superconductor's paired electrons.
Known as the Yu-Shiba-Rusinov state, or Shiba state for short, this state has been attracting a lot of interest because it could shed light on the emergence of a special state in a topological superconductor called the Majorana zero mode, which is promising for realizing fault-tolerant quantum computing.
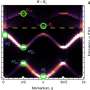
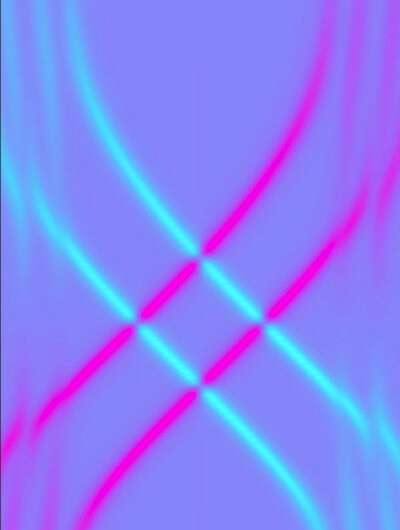
Experimentalists use scanning tunneling microscopes to probe superconductors with magnetic atoms on them. Controlling the distance between the microscope tip and the atom allows them to control how strongly the atom interacts with the superconductor. But one finding that has puzzled them is the observation that the Shiba states have two zero-energy crossings as the interaction is varied, which differs to theory predicting only one such crossing.
"So there's actually an inconsistency between theory and experiment," says Ching-Kai Chiu of the RIKEN Interdisciplinary Theoretical and Mathematical Sciences Program. "That's the motivation behind our study."
Now, by conducting a theoretical analysis of such a system, Chiu and his collaborator have discovered the origin of the double crossing.
They found that the interaction of the magnetic atom with the bulk states of the superconductor produces the double crossing. Previous analyses overlooked this because they considered only the surface states of the superconductor. "Our analysis has shown that you can't ignore the bulk theory," says Chiu. "You need to consider the entire system."
The two researchers achieved more than they had intended. "Initially, we didn't have any intention of explaining the two crossings," says Chiu. "It came as a real surprise to us. When we ran our simulations and we saw them, we thought it might have been an error. But further analysis showed that we had stumbled on the origins of the double crossing."
Based on their analysis, the pair proposes an experimental arrangement for scanning tunneling microscopy that should be able to distinguish between the two zero-energy crossings.
The paper is published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
More information: Ching-Kai Chiu et al, Yu-Shiba-Rusinov States in a Superconductor with Topological Z2 Bands, Physical Review Letters (2022). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.128.237001
Journal information: Physical Review Letters
Provided by RIKEN