Protective effects of ginsenoside CK against oxidative stress-induced neuronal damage
Oxidative stress is an important pathogenic mechanism in degenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease. Although ginsenoside compound K (CK) is protective against neuronal oxidative damage, the underlying mechanism remains to be understood.
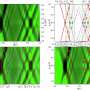
In an article published in Acta Materia Medica, the protective effects of ginsenoside CK against oxidative stress damage induced by hydrogen peroxide in HT22 cells were investigated with 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR)-based metabolomics.
The optimal CK concentration for decreasing oxidative stress damage in nerves was determined with MTT assays. CK (8 μM) significantly increased the HT22 cell survival rate after the model was established. Cell lysates were subjected to 1H-NMR metabolomics, western blotting, and ATP assays for verification.
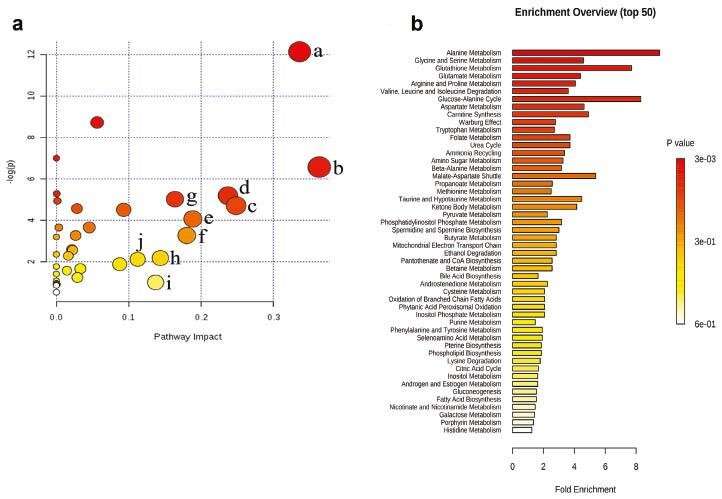
Metabolic perturbation occurred in HT22 cells in the model group but not the control group. Twenty biomarkers were identified and used to analyze metabolic pathways. CK reversed metabolic changes in HT22 cells by altering taurine, glutamate, glycine, and glutathione metabolism. Subsequently, CK increased ATP content and the expression of components of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in HT22 cells.
These findings demonstrate that CK prevents oxidative stress damage and protects nerves by regulating energy-metabolism pathways, such as those of taurine, glutamate, and other amino acids, thus providing a rationale for the use of CK in Alzheimer's disease treatment.
More information: Na Li et al, Protective effects of ginsenoside CK against oxidative stress-induced neuronal damage, assessed with 1H-NMR-based metabolomics, Acta Materia Medica (2022). DOI: 10.15212/AMM-2022-0009
Provided by Compuscript Ltd