Researchers identify ultrafast dynamics in monolayer MoS₂/ReSe₂ heterostructures
A collaborated team led by Prof. Su Fuhai from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) recently identified the ultrafast dynamics in monolayer MoS2/ReSe2 heterostructures.
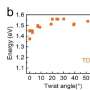
After studying the ultrafast carrier dynamics of this heterostructure, the researchers identified the relaxation pathways and intermediate processes of carrier transfer, free carrier evolution, and interlayer exciton, etc., within different time scales ranging from sub-picoseconds to hundreds of picoseconds. Results have been published in ACS Nano.
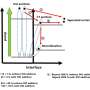
The construction of van der Waals (vdW) heterostructures, using different two dimensional (2D) transition-metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) films, provides a promising route to tailor the physical properties for individual layers and further extending their application prospects in photoelectric devices. Meanwhile, the understanding of photocarrier dynamics in vdW 2-D-TMDs, including different intermediate excitation species and relaxation pathways, plays essential roles for the development of devices.
The complete scenario of photocarrier dynamics, especially in the Rhenium dichalcogenides-based 2D-TMDs heterostructures having significances in the polarization sensitive photoelectric devices in near-infrared spectrum, remains elusive so far.
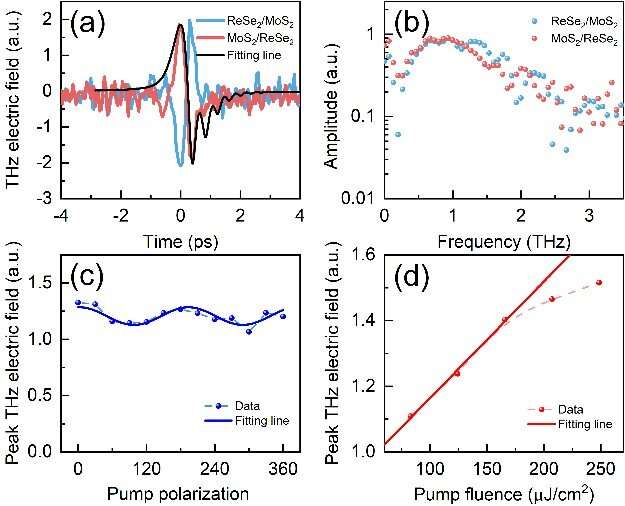
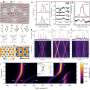
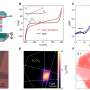
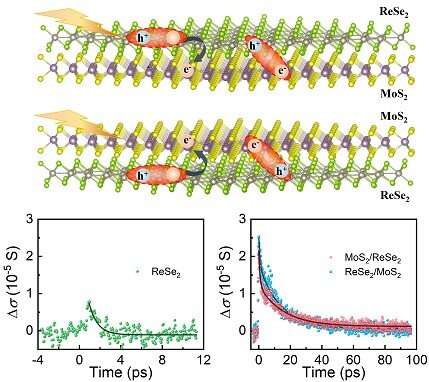
In this research, with large-scale vertically stacked heterostructures fabricated by their collaborators, the researchers investigated photocarriers dynamics via THz emission spectroscopy, time resolved THz spectroscopy and near-infrared optical pump probe spectroscopy, which allowed for the direct probe of out-of-plane charge transfer (CT), in-plane charge transport and interband transition, respectively.
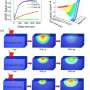
Supported by the theory calculations and simulations, they established the photocarrier dynamics pathway across charge separation, including the initial CT, intermediated evolution from free electron-hole plasma to interlayer excitons and free-carrier trapping, as well as the long-living interexcitons recombination.
CT tends to pronouncedly increase the transient THz photoconductivity (~2.8 times), nonlinear saturable absorption (~5 times) and interband recombination lifetime (> 10 times) in the heterostructures compared with the isolated ReSe2 monolayer, which is most interesting to them, as it demonstrated the large-range tunability in photocarrier dynamics basing on the heterostructures construction.
This work provides comprehensive insight into the photocarrier dynamics across the charge separation and it will help with the development of optoelectronic devices based on ReSe2-MoS2 heterostructures.
More information: Jin Yang et al, Identifying the Intermediate Free-Carrier Dynamics Across the Charge Separation in Monolayer MoS2/ReSe2 Heterostructures, ACS Nano (2021). DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.1c06822
Journal information: ACS Nano
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences