Intelligence emerging from random polymer networks
Reservoir computing (RC) tackles complex problems by mimicking the way information is processed in animal brains. It relies on a randomly connected network that serves as a reservoir for information and ultimately leads to more efficient outputs. For realizing RC directly in matter (instead of simulating it in a digital computer), numerous reservoir materials have been investigated to date. Now a team including researchers from Osaka University has designed a sulfonated polyaniline network for RC.
Neural networks in the brain use electrochemical signals carried by ions. Therefore, an electrochemical approach is a logical choice when choosing a material system for RC. Organic electrochemical field-effect transistors (OECFETs) are popular in bioelectronics; however, they have not yet been widely used for RC.
The key to the reservoir material is that it has rich (time-dependent) behavior and is disordered, which makes polymer materials an excellent option as they form random networks by themselves.
Polyaniline is a promising polymer for RC applications, because it is easy to polymerize, has good stability in the atmosphere, and has reversible doping/de-doping behavior, which means its conduction can be altered.
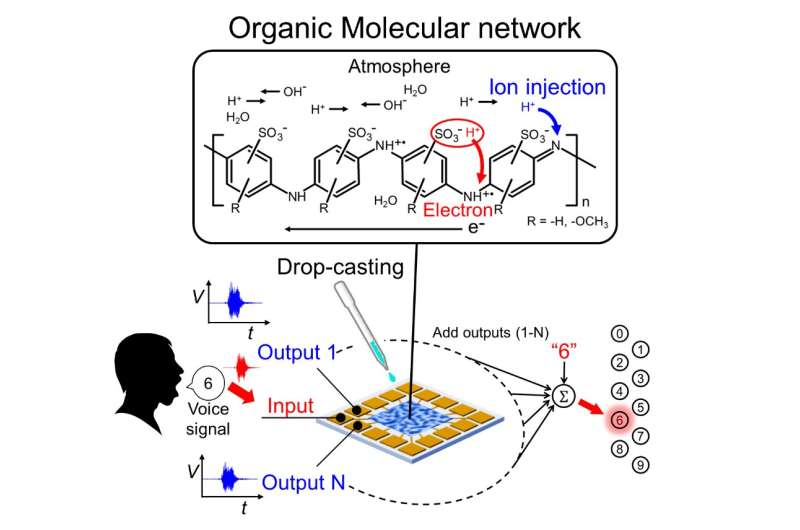
The researchers investigated sulfonated polyaniline (SPAN), which, in addition to the advantages of polyaniline, has high water-solubility and self-doping behavior. These make SPAN easier to work with and the doping more uniform.
"Atmospheric protons are injected directly into the polymer chain of SPAN, which causes it to conduct," explains study lead author Yuki Usami. "This conduction can then be controlled by adjusting the humidity."
The researchers used a simple drop-casting method to assemble the SPAN on gold electrodes to give an organic electrochemical network device (OEND).
The SPAN OEND was tested for RC by checking the waveform and assessing its performance in short-term memory tasks. Results of a test to see how well speech could be recognized achieved 70% accuracy. This ability of SPAN OEND was comparable with a software simulation of RC.
"We have shown that our SPAN OEND system can be applied in RC," says study corresponding author Takuya Matsumoto. "Future steps to establish systems that do not rely on humidity will provide more practical options; however, the success of our SPAN-based system is a positive step for material-based reservoir computing, which is expected to have a significant impact on the next generation of artificial intelligence devices."
More information: Yuki Usami et al, In‐Materio Reservoir Computing in a Sulfonated Polyaniline Network, Advanced Materials (2021). DOI: 10.1002/adma.202102688
Journal information: Advanced Materials
Provided by Osaka University