Boron quantum dots surpassing graphene with excellent thermal properties

In a new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances, researchers led by Professor Han Zhang from Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, China, consider whether boron quantum dots surpass the graphene in thermal properties.
The discovery of graphene in 2004 opened the door to the possibilities of two-dimensional materials. Various two-dimensional materials have been reported since, (black phosphorus, transition metal sulfides, topological insulators, MXene, etc.) but graphene is still widely studied due to its excellent optoelectronic properties. The thermal conductivity of pure single-layer graphene with few defects is as high as 5300 W/mK, which is the most potential thermal material known. As the properties of materials are closely related to their atomic structure it could be asked whether there are new materials with thermal properties exceeding that of graphene? Some researchers have used the non-equilibrium Greens function and the first-principles method to prove that the thermal conductivity of borophene can surpass that of graphene, implying that boron has high potential for thermal applications. Due to the difficulty of fabricating borophene, there have not been relevant experimental reports about the thermal properties to date. In this current article, Professor Han Zhang's research group describe the preparation of boron quantum dots, and indirectly proved the thermal properties of boron materials by combining thermo-optical switches. The results have been successfully applied to the fields of all-optical modulators and laser engineering. The authors' experiments prove that boron materials are promising for photothermal conversion and the thermal conducting applications exceed those of graphene. Further investigations of the thermal properties of borophene are planned by the research group.
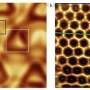
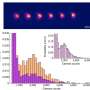
Professor Han Zhang's research group proposes the preparation of boron quantum dot material by the liquid-phase exfoliation method. The high-resolution electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy were used to prove the successful preparation of boron quantum dots. The thermography was used to record and analyze the photothermal conversion characteristics and the stability of the boron quantum dots. Experimental results show that boron quantum dots have excellent thermal stability (Figure 1a). The response time of the all-optical modulator based on the thermo-optical effect is closely related to the heat generation and thermal diffusion. The authors used this method to indirectly compare the photothermal characteristics of the boron material with that of graphene and successfully realized the all-optical phase and intensity modulator. The rise and fall times of the all-optical modulator based on graphene are 9.1 ms and 3.2 ms, respectively. In the experiment described by this paper, the rise and fall times of the all-optical modulator based on boron quantum dots are 1.1 ms and 1.3 ms respectively (Figure 1b). This proves that the thermal properties of boron quantum dots are better than that of graphene, with more researches required to investigate further. By applying the constructed all-optical modulator to the laser resonator, the optically controlled Q-switched laser operation is realized. Compared with the application of acousto-optic modulator and electro-optic modulator in the laser field, this work shows excellent monochromaticity (0.04 nm) and controllable frequency, which has potential applications in nonlinear frequency conversion and all-optical communication fields.
More information: Cong Wang et al, Boron quantum dots all-optical modulator based on efficient photothermal effect, Opto-Electronic Advances (2021). DOI: 10.29026/oea.2021.200032
Provided by Compuscript Ltd