The pulse of the Dead Sea
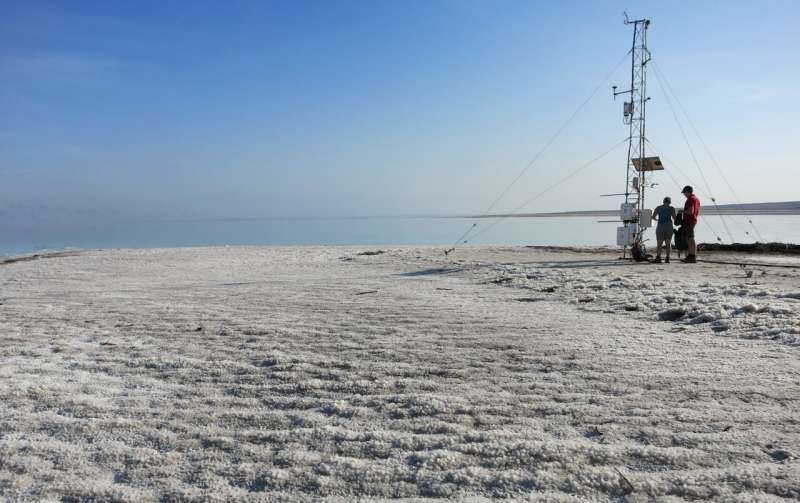

The Dead Sea is shrinking. There are many reasons for this: climate change is a contributing factor, as is human overuse of water as a resource. The sinking water level has a number of dangerous consequences. For example, fresh groundwater flowing downstream causes salts to dissolve in the soil, resulting in sinkholes. But it also leads to large-scale subsidence of the surrounding land surface. Researchers from an interdisciplinary team of several sections from the GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences, together with colleagues from Hannover, Kiel and Padua, have now for the first time demonstrated a direct link between the decrease in the water table, evaporation and land subsidence. They report on this in the journal Scientific Reports.
The team used a wide range of instruments; from measurement methods based on the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) to radar satellites and on-site gage and climate stations. The researchers showed that the solid earth moves up and down synchronously with fluctuations in the water surface and groundwater level with a time lag of about eight weeks. However, the trend is clearly in one direction: downward.
The water level of the Dead Sea sinks about one meter per year, and the land sinks about 15 centimeters per year. Inflows from rainfall in the surrounding mountains and the Jordan River cause short-term rises in the lake level. However, water withdrawals from the tributaries for agriculture, pumping of saline water to extract potassium, and evaporation in the high heat turn the balance permanently negative.
The coupling of land subsidence to the sinking water table has long been clear. But the fact that the movement of the land surface is so directly related to hydro-meteorological fluctuations is new. The researchers determined this connection within three years. For agriculture, tourism and infrastructure in the region, land subsidence and water loss are very threatening. The measurements show for the first time how closely land, water and atmosphere are linked here.
More information: Sibylle Vey et al, Delayed subsidence of the Dead Sea shore due to hydro-meteorological changes, Scientific Reports (2021). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-91949-y
Journal information: Scientific Reports
Provided by Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres