Improve photosynthesis performance via photosystem II-based biomimetic assembly

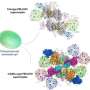
In the past decade, scientists have paid more attention to studying light harvest for producing novel bionic materials or integrating naturally biological components into synthetic systems. Tehir inspiration is the imitation of natural photosynthesis in green plants, algae, and cyanobacteria to convert light energy into chemical energy. Photosystem II (PSII) is a light-intervened protein complex responsible for the light harvest and water splitting to release O2, protons, and electrons. The development of PSII-based biomimetic assembly in vitro is useful for the investigation of photocatalysis, biological solar cells, and bionic photosynthesis.
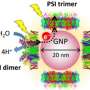
The combination of PSII and synthetic structures is useful for making biohybrid assemblies to harvest light. The evolution of material science advances the development of PSII-based assemblies, PSII-mimicking hybrid systems, and the utilization of PSII-related products for energy conversion. Relative applications and explorations occur by coupling PSII within lipid membranes, in multilayer polymeric structures, and in nanoparticles to maximize the efficient range of light absorbance and offer a high PSII payload yield.
At present, although reassembly of PSII-based hybrid systems is successful, this system suffers from typical drawbacks shared by common protein species in terms of stability, durability, biological activity, and environmental restrictions for applying PSII-based systems in the near future. Therefore, efforts and explorations are focused on investigating PSII-based biomimetic assembly to challenge these above weaknesses.
The article published in National Science Review by Prof. Junbai Li's group at Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Lab of Colloid, Interface and Chemical Thermodynamics, Institute of Chemistry of Chinese Academy of Sciences, summarizes recent studies on how PSII protein complex combines with artificial structures via molecular assembly, and highlights PSII-based semi-natural biosystems. Moreover, they discuss this biomimetic system's remaining problems, challenges, and outlooks.
More information: Mingjun Xuan et al, Photosystem II-based biomimetic assembly for enhanced photosynthesis, National Science Review (2021). DOI: 10.1093/nsr/nwab051
Provided by Science China Press