Selective concentration of cationic species

Sample pretreatment processes such as concentration or classification are essential to finding trace substances present in a fluid. In scientific communities recently, prolific research is being conducted on sample pretreatment techniques utilizing electrokinetics. However, due to the lack of commercial anion-permselective material—an essential component—its potential application is limited to only negatively charged particles. To this, a research team at POSTECH has found a way to isolate and concentrate only the cationic samples.
A POSTECH research team led by Professor Geunbae Lim, Ph.D. candidate Minsoo Lee, and Dr. Hyukjin J. Kwon of the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a novel type of multiscale-porous anion exchange membrane (MP-AEM) and successfully fabricated a convenient cation-permselective electrokinetic concentrator. Recognized for their excellence, these research findings were recently published as the cover paper in Advanced Functional Materials.
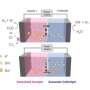
The ion exchange material serves to induce a strong electric field region in the channel through which the fluid flows by selectively passing ions of a specific polarity. Through this, charged particles present in the fluid are continuously concentrated by receiving electric repulsion force. In general, the polarity of the ion exchange material required differs depending on the polarity of the charged particles to be concentrated. A cation exchange material is required for negatively charged species, and an anion exchange material is required for positively charged species. However, unlike the cation exchange material that currently exists, there is no material that can be easily applied to the anion exchange material, complicating the fabrication of a cation concentrator.
To this, the research team successfully produced an anion exchange material that has a MP-AEM structure with excellent mechanical strength, ion exchange capacity, and fluid transport capacity through the simple casting and salt leaching method using the conventional anionic exchange materials.
The MP-AEM can be easily inserted into the electrokinetic concentrator using its peculiar property that allows simultaneous ion and fluid transport, successfully fulfilling the role of an anion exchange material. Accordingly, the research team was able to fabricate the cation-selective electrokinetic concentrator through a simple insertion and assembly method, which greatly streamlines the manufacturing process compared to the conventional method.
"The MP-AEM will play a major role in the vitalization and advancement of research fields involving cationic species," commented Professor Geunbae Lim. He added, "Considering the high scalability of the novel exchange membrane, it will be applicable to the areas of pollution control, resource recovery, and semiconductor cleaning as well as in the fields of diagnosis and detection of diseases."
More information: Minsoo Lee et al, A Multiscale‐Porous Anion Exchange Membrane for Convenient and Scalable Electrokinetic Concentration of Cationic Species, Advanced Functional Materials (2020). DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202006768
Journal information: Advanced Functional Materials
Provided by Pohang University of Science & Technology (POSTECH)