Image: Hubble captures eccentrically shaped NGC 1614 galaxy
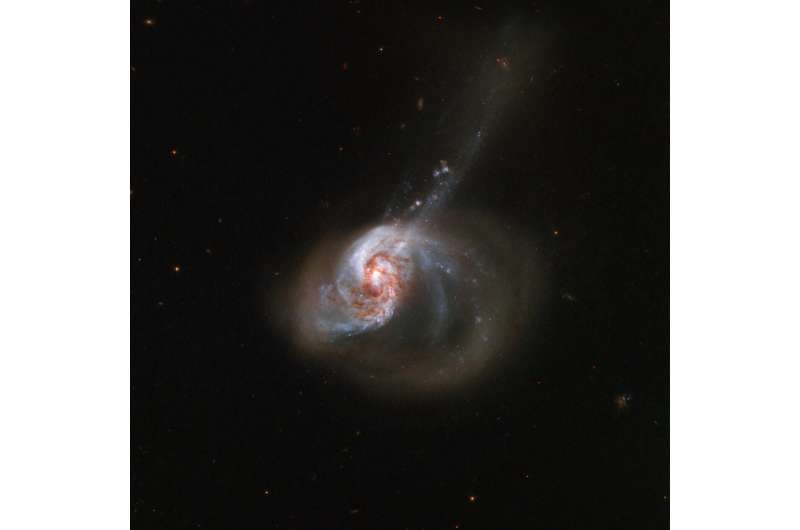

NGC 1614, captured here by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, is an eccentrically shaped galaxy ablaze with activity. The galaxy resides about 200 million light-years from Earth and is nestled in the southern constellation of Eridanus (the River).
NGC 1614 is the result of an active galactic merger, which creates its peculiar appearance, including a tidal tail. The cosmic collision also drives a turbulent flow of interstellar gas from the smaller of the two galaxies involved into the nucleus of the larger one, resulting in a burst of star formation that started in the core and has slowly spread outward through the galaxy.
Owing to its turbulent past and its current appearance, astronomers classify NGC 1614 as a peculiar galaxy, a starburst galaxy, and a luminous infrared galaxy. Luminous infrared galaxies are among the most luminous objects in the local universe—and NGC 1614 is, in fact, the second most luminous galaxy within 250 million light-years.
Provided by NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center