New E. coli-infecting bacteriophage introduced in PHAGE

A new coliphage—a bacteriophage that infects and can destroy Escherichia coli—is presented and characterized in PHAGE: Therapy, Applications, and Research.
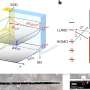
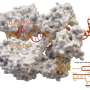
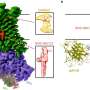
The article entitled "Genome Sequence and Characterization of Coliphage vB_Eco_SLUR29." was coauthored by Andrew Millard, University of Leicester, and colleagues from the University of Leicester, University of Warwick (Coventry), and University of Nottingham (Sutton Bonington), U.K. Coliphage have potential therapeutic applications, and more than 600 unique coliphage have been isolated and their genomes sequenced to date. The researchers isolated vB_Eco_SLUR29 from cattle slurry collected from a farm in rural England. They analyzed the ability of this novel coliphage to lyse E. coli and they sequenced its genome. They used transmission electron microscopy to identify the phase as a member of the Siphoviridae family, and they used physogenetic analysis and comparative genomics to identify it as part of a new genus within the subfamily Tunavirinae.
"In an increasing era of finding new phages that infect bacterial pathogens, it will be to our advantage as much as possible to systematically catalogue genomic and biological data collected on new phages," said Martha Clokie, Ph.D., Editor-in-Chief of PHAGE and Professor of Microbiology, University of Leicester (U.K.). "To present newly isolated and characterized phages, we suggest they are written up as 'phage introductions.' I am very pleased that Andy Millard—who coined this concept—has written a key exemplar paper to showcase our first 'introduction.' Please meet coliphage vB_Eco_SLUR29!"
More information: Ibrahim Besler et al, Genome Sequence and Characterization of Coliphage vB_Eco_SLUR29, PHAGE (2020). DOI: 10.1089/phage.2019.0009
Provided by Mary Ann Liebert, Inc