Mosquito eye inspires artificial compound lens
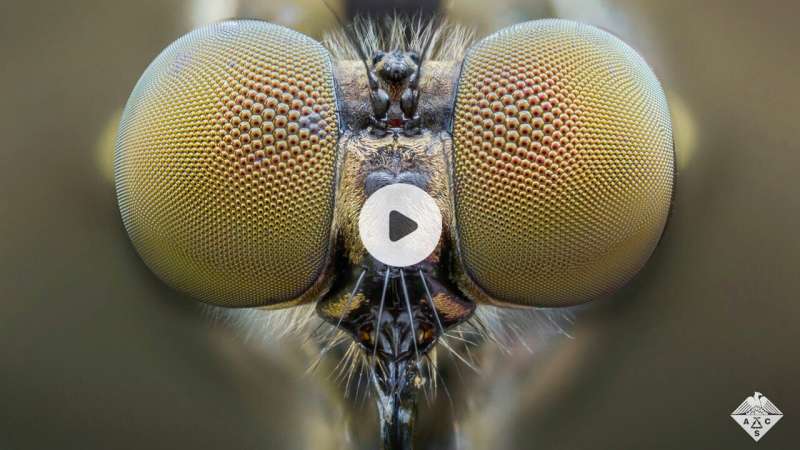

Anyone who's tried to swat a pesky mosquito knows how quickly the insects can evade a hand or fly swatter. The pests' compound eyes, which provide a wide field of view, are largely responsible for these lightning-fast actions. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces have developed compound lenses inspired by the mosquito eye that could someday find applications in autonomous vehicles, robots or medical devices.
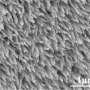
Compound eyes, found in most arthropods, consist of many microscopic lenses organized on a curved array. Each tiny lens captures an individual image, and the mosquito's brain integrates all of the images to achieve peripheral vision without head or eye movement. The simplicity and multifunctionality of compound eyes make them good candidates for miniaturized vision systems, which could be used by drones or robots to rapidly image their surroundings. Joelle Frechette and colleagues wanted to develop a liquid manufacturing process to make compound lenses with most of the features of the mosquito eye.
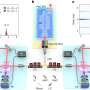
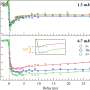
To make each microlens, the researchers used a capillary microfluidic device to produce oil droplets surrounded by silica nanoparticles. Then, they organized many of these microlenses into a closely packed array around a larger oil droplet. They polymerized the structure with ultraviolet light to yield a compound lens with a viewing angle of 149 degrees, similar to that of the mosquito eye. The silica nanoparticles coating each microlens had antifogging properties, reminiscent of nanostructures on mosquito eyes that allow the insect organs to function in humid environments. The researchers could move, deform and relocate the fluid lenses, allowing them to create arrays of compound lenses with even greater viewing capabilities.
More information: Donglee Shin et al. Multifunctional Liquid Marble Compound Lenses, ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces (2019). DOI: 10.1021/acsami.9b12738
Journal information: ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces
Provided by American Chemical Society