Scientists develop highly sensitive molecular optical pressure sensor

Chemists at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) and at the Université de Montréal in Canada have developed a molecular system capable of very precise optical pressure measurements.
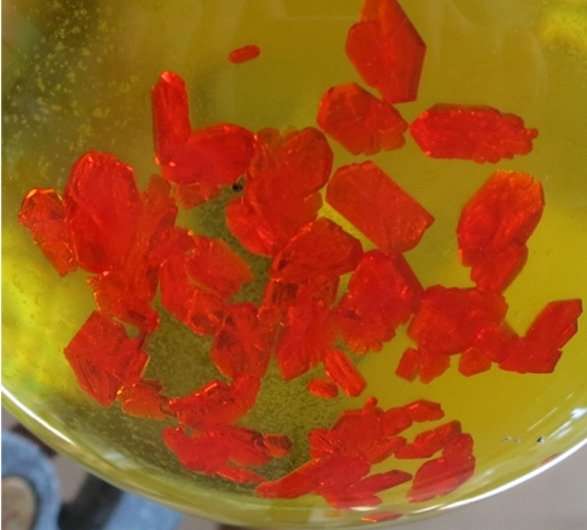
The gemstone ruby served as the source of inspiration. However, the system developed by the team headed by Professor Katja Heinze at the JGU Institute of Inorganic Chemistry and Analytical Chemistry and Professor Christian Reber at the Université de Montréal is a water-soluble molecule, not an insoluble solid. Like ruby, this molecule contains the element chromium that gives it its red color, and it has thus been dubbed molecular ruby. This molecular ruby can be used to measure pressure both in the solid state as the gemstone ruby and in solution thanks to its solubility. Thus, this molecular system has potential applications in the fields of materials sciences, homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis, and all conceivable fields where pressure changes need to be monitored. The research findings have recently been published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
Measuring the pressure with the molecular ruby is very straightforward. The relevant site is irradiated with blue light to be absorbed by the molecular ruby, which then emits infrared radiation. Depending on the pressure, the energy of the emitted light varies in a very sensitive manner. The actual pressure can then be read from the luminescence energy.
The sophisticated pressure-dependent luminescence measurements up to 45,000 bar have been performed by Sven Otto, a doctoral candidate in Heinze's team, in the laboratories of the Reber group at the Université de Montréal. Sven Otto's research stay was funded by the Materials Science in Mainz (MAINZ) Graduate School of Excellence. "The experimental work in Montréal was a great experience and the successful proof of concept was just fantastic," said Otto. "The highest pressures employed in a so-called diamond anvil cell are roughly 45 times higher than that experienced at the deepest known spot in the ocean", explained Otto. "The very large effects observed with this molecular material are really stunning," added Profoessor Christian Reber, an expert in high-pressure luminescence spectroscopy and currently a DAAD guest scientist at Mainz University, funded by the German Academic Exchange Service. In fact, the effects are up to twenty times larger with the molecular ruby crystals than with the commonly employed gemstone ruby.
The principle of optical pressure measurements using chromium based materials is not new. However, until now, all these materials have been completely insoluble like ruby. Pressure measurements with a single type of dissolved molecular species reporting pressure changes directly in solution had not yet been achieved. "However, our molecular ruby can do the trick," said Professor Katja Heinze. "We hope that our findings will pave the way for completely different applications beyond the classical ones and we are currently working in this direction."
More information: Sven Otto et al, Molecular ruby under pressure, Angewandte Chemie International Edition (2018). DOI: 10.1002/anie.201806755
Journal information: Angewandte Chemie International Edition
Provided by Universitaet Mainz