Plenty of habitat for bears in Europe
Great opportunity for European brown bears: A new study spearheaded by the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv) and the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) shows that there are still many areas in Europe where bears are extinct, but with suitable habitat for hosting them. Effective management of the species, including a reduction of direct pressures by humans (like hunting) has the potential to help these animals come back in many of these areas, according to the head of the study. It is now important to plan the recovery of the species while taking measures to prevent conflicts.
Some 500 years ago, there were brown bears almost everywhere in Europe. However, in the following centuries, they were wiped out in many places, including Germany. The reasons for the decline of bears were primarily habitat loss and hunting. Today, around 17,000 animals still live in Europe, distributed over 10 populations and 22 countries. Some of these populations are at risk due to their relatively small size.
Excellent opportunity for species conservation
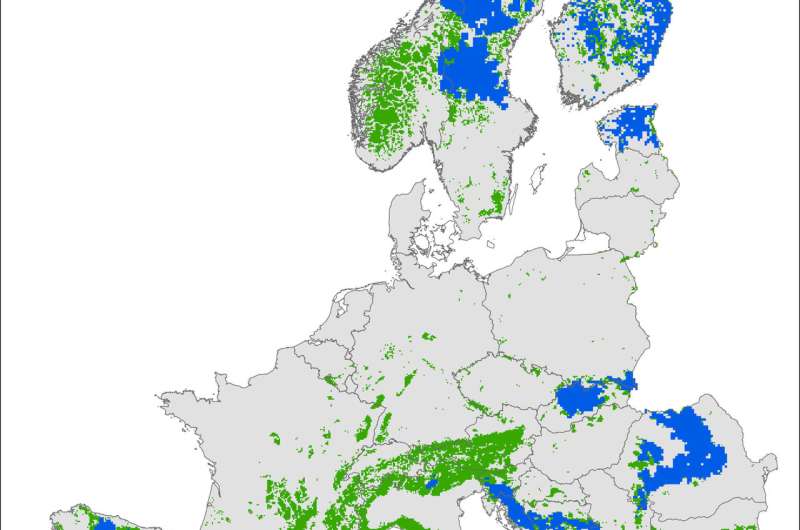
In recent years, the hunting of brown bears has been banned or restricted in Europe, and in the future, bears could recolonise parts of the continent. A new study led by the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv) and Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) reveals that there are still many areas in Europe where there are currently no bears, but which would, in principle, be suitable as habitat. Of an estimated amount of more than 1 million square kilometres of suitable habitat in Europe, about 37 percent is not populated, equivalent to an area of about 380,000 square kilometres. In Germany, there are 16,000 square kilometres of potential bear habitat. However, the probability of future recolonisation varies widely. For example, in Germany, potential bear habitats outside the Alps are geographically isolated and unlikely to be recolonized naturally.

"The fact that there is still suitable habitat for brown bears is a great opportunity for species conservation," says the head of the study, Dr. Néstor Fernández from the iDiv research centre and the University of Halle. Scientists are already seeing around 70 percent of Europe's populations recover, and it is likely that bears will return to some of the currently unoccupied areas. "In Germany, too, it is very likely that some areas will, sooner or later, be colonised by brown bears, especially in the Alpine region," says Fernández. So, there is reason to hope that bears will be native to Germany once more, 200 years after their extermination.
Pre-emptive action important
For many people, this would probably be good news. "In recent years, the attitude of Europeans towards wildlife has changed a lot. Today, many people feel positive about the return of large mammals," says Fernández. Nevertheless, the fact that bear comeback can lead to conflicts with some human activities needs to be considered at an early stage. Such conflicts mostly arise when bears eat crops or damage beehives, and they also occasionally attack sheep. Direct attacks by bears on humans are, however, extremely rare; bears themselves generally steer clear of people.

The map developed by Fernández and his colleague Anne Scharf (Max Planck Institute for Ornithology) makes it possible to predict the areas into which bears could return. These maps can help policymakers identify potential areas of conflict early and counter these with specifically targeted measures. For example, compensation payments should be coupled with preventive measures being taken in advance, explains Fernández. Such preventive measures can be, for example, the construction of physical barriers such as closures for apiaries, electric fences, or the use of guard dogs to protect fields and grazing pastures, and increasing public awareness. A look at the map also makes it clear that bears do not stick to national borders. "That's why a common management policy for the brown bear and other wild animals at the European level would be desirable," says Fernández. At present, policies between member states regarding the protection and management of bears is very heterogeneous, and there is disparity in how compensation schemes are structured in different states.
For their study, Scharf and Fernández have collated the results of all relevant previous bear habitat studies. These each focused on a delimited area in which bears live, and, for this area, analysed which requirements the animals have for their habitat. By bringing together the results of these local studies, the scientists were able to create a computer model that would identify further potential bear habitat across Europe. The predictions made by this model are more reliable than if the data from one region were merely applied to the whole of Europe. Scharf and Fernández have published their results in the journal Diversity and Distributions .
More information: Anne K. Scharf et al, Up-scaling local-habitat models for large-scale conservation: Assessing suitable areas for the brown bear comeback in Europe, Diversity and Distributions (2018). DOI: 10.1111/ddi.12796
Journal information: Diversity and Distributions
Provided by German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv) Halle-Jena-Leipzig