Preventing psoriasis with vanillin
Small amounts of artificial vanilla extract, also known as vanillin, are in a wide range of products, from baked goods to perfumes. But vanillin's versatility doesn't stop there. In a recent mouse study reported in ACS' Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, researchers report that this compound could also prevent or reduce psoriatic skin inflammation.
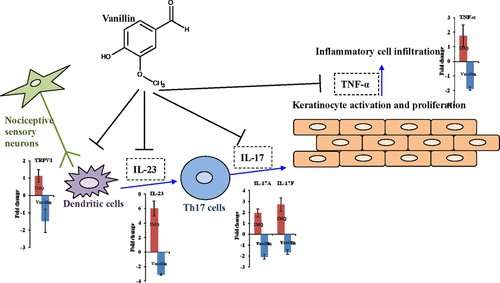
Psoriasis is an inflammatory skin disorder that affects about 125 million people worldwide, resulting in scaly red plaques that typically show up on the elbows, knees or scalp. Immune system proteins called interleukins (IL) 17 and 23 are known to be key players in the development of the condition. Interestingly, vanillin can have effects on different interleukins that are involved in other inflammatory conditions and diseases. So, Chien-Yun Hsiang and Tin-Yun Ho wanted to see if treatment with vanillin could prevent psoriatic symptoms.
The researchers induced psoriatic skin inflammation on groups of mice by putting a compound called imiquimod on their skin. In addition, the mice were orally given daily doses (0, 1, 5, 10, 50 or 100 milligrams/kilograms of body weight) of vanillin for seven days. Mice treated with 50- or 100-milligram/kilograms of body weight doses had reduced psoriatic symptoms compared to those receiving smaller or no doses of vanillin. In all mice treated with vanillin, IL-17 and IL-23 protein levels were decreased. The researchers say that vanillin was an effective compound against psoriatic skin inflammation in this animal model.
More information: Hui-Man Cheng et al. Oral Administration of Vanillin Improves Imiquimod-Induced Psoriatic Skin Inflammation in Mice, Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry (2017). DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b04259
Abstract
Vanillin is one of the most widely used flavoring products worldwide. Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder. The interleukin-23 (IL-23)/interleukin-17 (IL-17) axis plays a critical role in psoriasis. Here, we analyzed the effect of vanillin on imiquimod (IMQ)-induced psoriatic skin inflammation in mice. Mice were treated topically with IMQ on the back skin and orally with various amounts of vanillin for 7 consecutive days. Vanillin significantly improved IMQ-induced histopathological changes of skin in a dose-dependent manner. The thickness and number of cell layers of epidermis were reduced by 29 ± 14.4 and 27.8 ± 11%, respectively, in mice given 100 mg/kg of vanillin. A microarray showed that a total of 9042 IMQ-upregulated genes were downregulated by vanillin, and the biological pathways involved in the immune system and metabolism were significantly altered by vanillin. The upregulated expressions of IL-23, IL-17A, and IL-17F genes were suppressed by vanillin, with fold changes of −3.07 ± 0.08, −2.06 ± 0.21, and −1.62 ± 0.21, respectively. Moreover, vanillin significantly decreased both the amounts of IL-17A and IL-23 and the infiltration of immune cells in the skin tissues of IMQ-treated mice. In conclusion, our findings suggested that vanillin was an effective bioactive compound against psoriatic skin inflammation. Moreover, the downregulation of IL-23 and IL-17 expression suggested that vanillin was a novel regulator of the IL-23/IL-17 axis.
Journal information: Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
Provided by American Chemical Society