High speed video recording precisely measures blood cell velocity
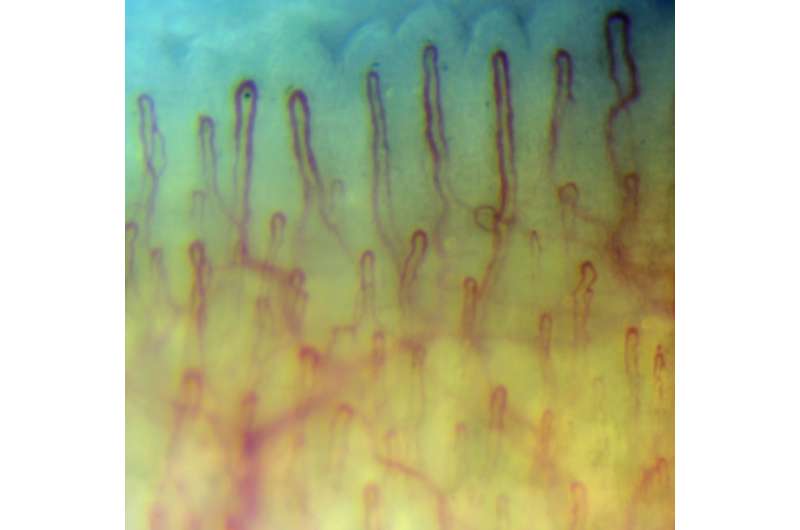
Scientists from ITMO University created a high-speed video capillaroscopy system that enables direct measurement of red blood cell velocity. Coupled with sophisticated software, the system can improve the accuracy of vascular condition assessment. Such a system could be useful for monitoring the efficiency of certain therapies. The results of the research were published in Optics and Lasers in Engineering.
Capillaroscopy systems are commonly used either to determine the shape and size of a single capillary or to examine some specific part of a capillary network. Geometric patterns that emerge from capillary structures, as well as blood cell velocity, can reflect the condition of the entire vascular system. Although blood cell velocity is among crucial diagnostic parameters, its direct and precise measurement is not an easy task.
In the study, researchers from ITMO University applied high-speed video recording of red blood cells in the capillary to measure blood flow velocity. The system relies on the combination of optical equipment with specially designed data processing software. A microscope coupled with a high-speed video camera captures the image of capillaries. The frame sequence is then processed in order to restore the capillaries' shape and configuration as well as to determine the distance that blood cells cover per time unit. Besides being useful for diagnostics, such data may help to assess whether a certain therapy is efficient or not.
"In addition to shape and diameter of each capillary, we can determine how fast red blood cells flow through each capillary in the capillary net," says Igor Gurov, lead author and head of the Center For Computational Optics, Photonics and Imaging at ITMO University. "Although relatively simple, our device is capable of providing reliable data that can be extremely useful for disease patterns recognition. What is more, such a diagnostic procedure is absolutely painless, safe and comfortable for patients."
Retrieving blood flow velocity data is important when it comes to such diseases as diabetes or coronary heart disease. "Flow velocity is a primary factor in estimating the condition of any tissue by its blood supply. For instance, in diabetes, the circulation speed may alter even though blood vessels generally appear to be normal. Our main task now is to use the system to address socially significant diseases. In particular, the system can be an effective tool for studying what happens in blood vessels during coronary heart disease and how drugs affect blood flow recovery," explains one of the authors Nikita Margariants.
By and large, other methods of measuring blood flow velocity cannot provide highly accurate data and do not allow for long-term measurements. "There are alternative devices that can only give a rough average estimate of blood cell velocity," says Mikhail Volkov, researcher at the Center For Computational Optics, Photonics and Imaging.
The authors emphasize that the development of image recording and processing facilities will significantly expand the capabilities of the new system. "As new video cameras, exchange buses and software appear, this method will become better and more accurate. Time is on our side," points out Mikhail Volkov.
More information: Igor Gurov et al, High-speed video capillaroscopy method for imaging and evaluation of moving red blood cells, Optics and Lasers in Engineering (2017). DOI: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2017.09.003
Provided by ITMO University