Genetic engineering tool generates antioxidant-rich purple rice
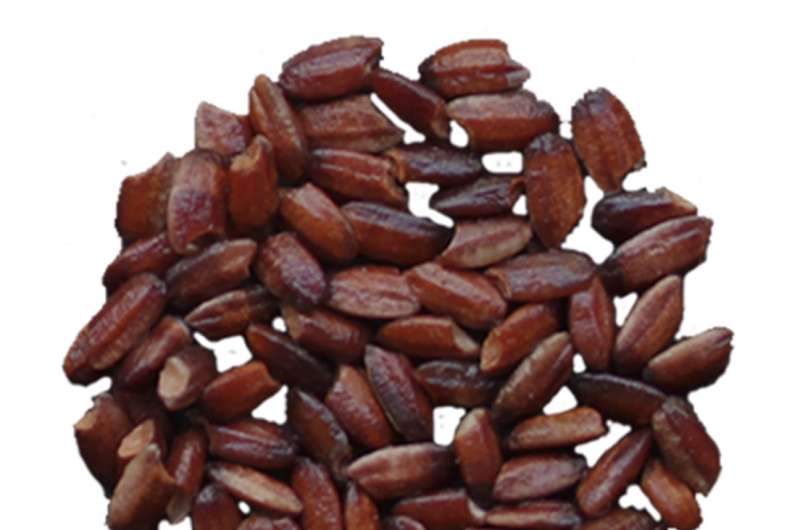

Researchers in China have developed a genetic engineering approach capable of delivering many genes at once and used it to make rice endosperm—seed tissue that provides nutrients to the developing plant embryo—produce high levels of antioxidant-boosting pigments called anthocyanins. The resulting purple endosperm rice holds potential for decreasing the risk of certain cancers, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and other chronic disorders. The work appears June 27th in the journal Molecular Plant.
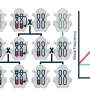
"We have developed a highly efficient, easy-to-use transgene stacking system called TransGene Stacking II that enables the assembly of a large number of genes in single vectors for plant transformation," says senior study author Yao-Guang Liu of the South China Agricultural University. "We envisage that this vector system will have many potential applications in this era of synthetic biology and metabolic engineering."
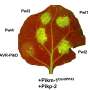
To date, genetic engineering approaches have been used to develop rice enriched in beta-carotene and folate, but not anthocyanins. Although these health-promoting compounds are naturally abundant in some black and red rice varieties, they are absent in polished rice grains because the husk, bran, and germ have been removed, leaving only the endosperm.
Previous attempts to engineer anthocyanin production in rice have failed because the underlying biosynthesis pathway is highly complex, and it has been difficult to efficiently transfer many genes into plants.
To address this challenge, Liu and his colleagues first set out to identify the genes required to engineer anthocyanin production in the rice endosperm. To do so, they analyzed sequences of anthocyanin pathway genes in different rice varieties and pinpointed the defective genes in japonica and indica subspecies that do not produce anthocyanins.
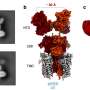
Based on this analysis, they developed a transgene stacking strategy for expressing eight anthocyanin pathway genes specifically in the endosperm of the japonica and indica rice varieties. The resulting purple endosperm rice had high anthocyanin levels and antioxidant activity in the endosperm. "This is the first demonstration of engineering such a complex metabolic pathway in plants," Liu says.
In the future, this transgene stacking vector system could be used to develop plant bioreactors for the production of many other important nutrients and medicinal ingredients. For their own part, the researchers plan to evaluate the safety of purple endosperm rice as biofortified food, and they will also try to engineer the biosynthesis of anthocyanins in other crops to produce more purple endosperm cereals.
"Our research provides a high-efficiency vector system for stacking multiple genes for synthetic biology and makes it potentially feasible for engineering complex biosynthesis pathways in the endosperm of rice and other crop plants such as maize, wheat, and barley," Liu says.
More information: Molecular Plant, Zhu et al.: "Development of ''Purple Endosperm Rice'' by Engineering Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in the Endosperm with a High-Efficiency Transgene Stacking System" www.cell.com/molecular-plant/a … 1674-2052(17)30140-5 , DOI: 10.1016/j.molp.2017.05.008
Journal information: Molecular Plant
Provided by Cell Press