How hydras know where to regrow lost body parts
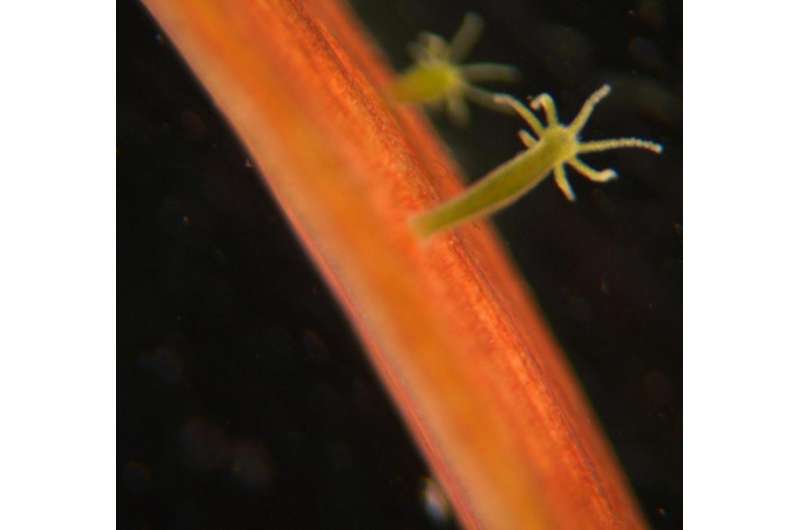

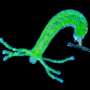
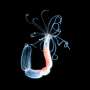
Few animals can match the humble hydra's resilience. The small, tentacled freshwater animals can be literally shredded into pieces and regrow into healthy animals. A study published February 7 in Cell Reports suggests that pieces of hydras have structural memory that helps them shape their new body plan according to the pattern inherited by the animal's "skeleton." Previously, scientists thought that only chemical signals told a hydra where its heads and/or feet should form.
Regenerating hydras use a network of tough, stringy protein fibers, called the cytoskeleton, to align their cells. When pieces are cut or torn from hydras, the cytoskeletal pattern survives and becomes part of the new animal. The pattern generates a small but potent amount of mechanical force that shows cells where to line up. This mechanical force can serve as a form of "memory" that stores information about the layout of animal bodies. "You have to think of it as part of the process of defining the pattern and not just an outcome", says senior author, biophysicist Kinneret Keren of the Technion- Israel Institute of Technology.
When pieces of hydra begin the regeneration process, the scraps of hydra fold into little balls, and the cytoskeleton has to find a balance between maintaining its old shape and adapting to the new conditions. "If you take a strip or a square fragment and turn it into a sphere, the fibers have to change or stretch a lot to do that," explains Keren. However, some portions retain their pattern. As the little hydra tissue ball stretches into a tube and grows a tentacle-ringed mouth, the new body parts follow the template set by the cytoskeleton in fragments from the original hydra.
The main cytoskeletal structure in adult hydra is an array of aligned fibers that span the entire organism. Tampering with the cytoskeleton is enough to disrupt the formation of new hydras, the researchers found. In many ways, the cytoskeleton is like a system of taut wires that helps the hydra keep its shape and function. In one experiment, the researchers cut the original hydra into rings which folded into balls that contained multiple domains of aligned fibers. Those ring-shaped pieces grew into two-headed hydras. However, anchoring the hydra rings to stiff wires resulted in healthy one-headed hydras, suggesting that mechanical feedbacks promote order in the developing animal.
Hydras are much simpler than most of their cousins in the animal kingdom, but the basic pattern of aligned cytoskeletal fibers is common in many organs, including human muscles, heart, and guts. Studying hydra regeneration may lead to a better understanding of how mechanics integrate with biochemical signals to shape tissues and organs in other species. "The actomyosin cytoskeleton are the main force generator across the animal kingdom," says Keren. "This is very universal."
More information: Cell Reports, Livshits and Shani-Zerbibet al.: "Structural inheritance of the actin cytoskeletal organization determines the body axis in regenerating Hydra" www.cell.com/cell-reports/full … 2211-1247(17)30073-6 , DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.01.036
Journal information: Cell Reports
Provided by Cell Press