The most advanced quantum algorithm known
An international research collaborative has published a paper in the prestigious journal Nature Communications titled "Digital quantum simulation of fermionic models with a superconducting circuit." The paper reports on the performance of the most advanced quantum algorithm known and which achieves the implementation of a quantum simulation of electronic models of materials in superconducting circuits. This algorithm has been developed at the superconducting circuit laboratories of Google/UCSB on the basis of original ideas proposed by the UPV/EHU QUTIS group.
The team of researchers in the UPV/EHU QUTIS Group who have participated in this project were led by the Ikerbasque professor Enrique Solano with the participation of Dr Lucas Lamata and PhD student Laura García-Álvarez.
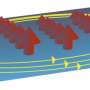
The collaboration between the UPV/EHU and Google/UCSB has produced a digital fermionic simulator in excess of 300 quantum logic gates on four superconducting quantum bits. Fermions are quantum particles such as electrons, which are the fundamental basis of superconductors, chemical reactions and high-energy processes. Accordingly, the current study is tremendously important, as it is the first one in which electrons are simulated in a universal way with such an advanced architecture and in a scalable way, as is the case of superconducting circuits at cryogenic temperatures.
Enrique Solano says, "this experiment represents the first digital simulator on a solid-state quantum platform, superior to the most advanced quantum algorithm made on a quantum computer which promises to revolutionise 21st-century information technologies."
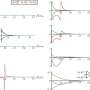
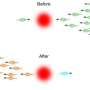
As detailed in the paper published in Nature Communications, one of the main applications of quantum information is the simulation of nature. Fermions are everywhere in nature, appearing in condensed-matter systems, chemistry and high-energy physics. Nevertheless, there is no doubt that universally simulating their interactions constitutes one of the greatest challenges facing physical chemistry and materials science.
The international echo of this achievement has been so significant that even the Google Research Blog, which covers the American multinational's research activities, has published an article on the collaboration, highlighting the work led by Enrique Solano. "Coming up with an efficient sequence of logic gates that can accurately model the interactions for systems of fermions wasn't easy. So we teamed up with the QUTIS group at the University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU), who are experts in constructing algorithms and translating them into streams of logic gates we can implement with our hardware," said the Google Research Blog through Prof John Martinis, leader of the experimental group, Dr Rami Barends, and the PhD student Julian Kelly.
More information: R. Barends et al. Digital quantum simulation of fermionic models with a superconducting circuit, Nature Communications (2015). DOI: 10.1038/ncomms8654
Journal information: Nature Communications
Provided by University of the Basque Country