Banded mongooses structure monosyllabic sounds in a similar way to humans
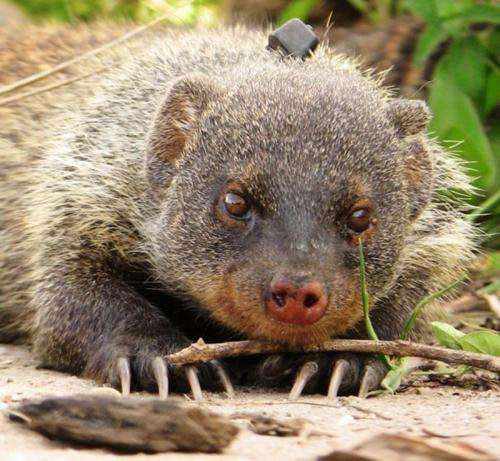

Animals are more eloquent than previously assumed. Even the monosyllabic call of the banded mongoose is structured and thus comparable with the vowel and consonant system of human speech. Behavioral biologists from the University of Zurich have thus become the first to demonstrate that animals communicate with even smaller sound units than syllables.
When humans speak, they structure individual syllables with the aid of vowels and consonants. Due to their anatomy, animals can only produce a limited number of distinguishable sounds and calls. Complex animal sound expressions such as whale and bird songs are formed because smaller sound units – so-called "syllables" or "phonocodes" – are repeatedly combined into new arrangements. However, it was previously assumed that monosyllabic sound expressions such as contact or alarm calls do not have any combinational structures. Behavioral biologist Marta Manser and her doctoral student David Jansen from the University of Zurich have now proved that the monosyllabic calls of banded mongooses are structured and contain different information. They thus demonstrate for the first time that animals also have a sound expression structure that bears a certain similarity to the vowel and consonant system of human speech.

Single syllable provides information on the identity and activity of the caller
The research was conducted on wild banded mongooses at a research station in Uganda. For their study, the scientists used a combination of detailed behavior observations, recordings of calls and acoustic analyses of contact calls. Such a call lasts for between 50 and 150 milliseconds and can be construed as a single 'syllable'. Jansen and his colleagues now reveal that, despite their brevity, the monosyllabic calls of banded mongooses exhibit several temporally segregated vocal signatures. They suspected that these were important so studied the individual calls for evidence of individuality and behavior. "The initial sound of the call provides information on the identity of the animal calling," explains Jansen. The second more tonal part of the call, which is similar to a vowel, however, indicates the caller's current activity.
Structured single syllables in animals not an exception?
Manser and her team are thus the first to demonstrate that animals also structure single syllables – much like vowels and consonants in human speech. The researchers are convinced that the banded mongoose is not the only animal species that is able to structure syllables. They assume that the phenomenon was overlooked in scientific studies thus far. For instance, they point out that frogs and bats also structure single syllables. "The example of banded mongooses shows that so-called simple animal sound expressions might be far more complex than was previously thought possible."
More information: David A.W.A.M. Jansen, Michael A. Cant, and Marta B. Manser. Segmental concatenation of individual signatures and context cues in banded mongoose (Mungos mungo) close calls. BMC Biology. doi:10.1186/1741-7007-10-97
Provided by University of Zurich