Streamflow changes following the 2010 Chile earthquake
Changes in streamflow and groundwater levels are known to occur following earthquakes. But the mechanisms for the changes in streamflow are not fully understood and vary from one location to another.
Mohr et al. investigated streamflow response in small upland catchments in south central Chile following the magnitude 8.8 Chilean earthquake on 27 February 2010.
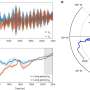
Streamflow initially decreased after the quake, then increased to as much as 400 percent of pre-earthquake levels. The increases peaked hours to several days following the earthquake, after which flow gradually declined, though changes were not uniform across all the catchments the authors studied.
Where did the excess water come from? Several factors suggest to the authors that extra water came from the interface between the sandy saprolite layers and the bedrock. The earthquake main shock produced enough energy that the sandy layer could have acted as a liquid.
Vertical permeability may also have increased, allowing a more efficient discharge of the water from the saprolite layer, which in turn enlarged the saturated zone and thereby enhanced streamflow.
In addition, the extra released water elevated the ground water table, which enhanced plant transpiration.
More information: “Streamflow response in small upland catchments in the Chilean coastal range to the MW 8.8 Maule earthquake on 27 February 2010” Journal of Geophysical Research-Earth Surface, doi:10.1029/2011JF002138 , 2012.
Provided by American Geophysical Union