Researchers take steps toward fast, low-cost DNA sequencing device
Researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory and Yale University have developed a new concept for use in a high-speed genomic sequencing device that may have the potential to substantially drive down costs.
"The low cost--if it can be achieved--would enable genomic sequencing to be used in everyday clinical practice for medical treatments and preventions," said Predrag Krstic, project director and former ORNL physicist now at the University of Tennessee-ORNL Joint Institute for Computational Sciences.
The research is part of a nearly decade-long drive by the National Human Genome Research Institute of the National Institutes of Health to support the science needed to bring the cost of sequencing a human genome down to $1,000.
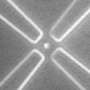
ORNL and Yale University researchers have created nanopores, or extremely narrow channels of water, with a radio-frequency electric field capable of trapping segments of DNA and other biomolecules.
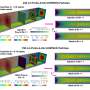
In a paper published in the scientific journal Small, titled, "Tunable Aqueous Virtual Micropore," ORNL and Yale University researchers used theory and computation, validated by experiments, to prove that a charged micro or nano particle, such as a DNA segment, can be confined in an "aqueous virtual pore." The water provides a stable environment for DNA integrity while the virtual "walls" allow DNA to move through the nanopore without interacting with physical walls.
As an added advantage, scientists can control the size and stability of a virtual nanopore by external electric fields, something they cannot do with a physical nanopore.
"As a single DNA polymer is translocated through a synthetic nanopore, we use the physical detection of single molecules to read electric signals that identify DNA bases," Krstic said.
To help control and localize DNA, ORNL and Yale scientists created the aqueous nanopore embedded in water based on a linear Paul trap – a device that traps particles in an oscillating electric field – and experimentally proved its trapping functionality.
There were some doubts that a charged micro or nano particle could be confined by the quadrupole oscillating electric field of the Paul trap when filled by aqueous solvent, but ORNL computation and Yale experiments prove that water actually helps stabilize trapping mechanisms, making sequencing methods more feasible.
Provided by Oak Ridge National Laboratory