Last update:
Bio & Medicine news

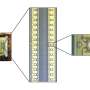
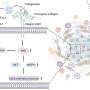
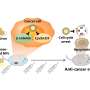
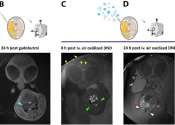
Designing a tiny new tool to map and treat children's brain cancer
Medulloblastoma is the most common cancerous brain tumor in children, and fighting it requires an approach that is delicate, durable, and direct. Now a group of researchers at UQ's Australian Institute for Bioengineering ...
Bio & Medicine
1 hour ago
0
0

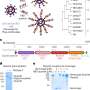
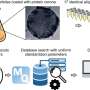
Scientists' new drug-delivery technology is possible breakthrough for multi-strain vaccines
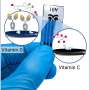
A new way to deliver drugs using a common protein could be used to develop mosaic vaccines, which are vaccines effective against multiple strains of a virus like COVID-19, among other medicines in a global first.
Bio & Medicine
1 hour ago
0
10

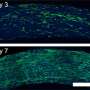
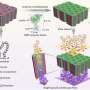
Lipid nanoparticle-mRNA regimen reverses inflammation and aids recovery from diabetic wounds in mice
Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have designed a regenerative medicine therapy to speed up diabetic wound repair. Using tiny fat particles loaded with genetic instructions to calm down inflammation, ...
Bio & Medicine
21 hours ago
0
70

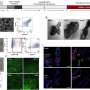
Study reveals promising development in cancer-fighting nanotechnologies
A new study conducted by the Wilhelm Lab at the University of Oklahoma examines a promising development in biomedical nanoengineering. Published in Advanced Materials, the study explores new findings on the transportation ...
Bio & Medicine
23 hours ago
0
7

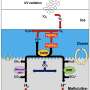
Improved ultrasound wireless charging for implantable biomedical devices
Ultrasound-based wireless power transfer is becoming a more attractive option to power implanted biomedical devices because it could overcome many of the limitations and challenges facing other wireless charging approaches. ...
Bio & Medicine
May 20, 2024
0
18

Method for producing sulfur compounds in cells shows promise for tissue repair
Sulfur-based compounds produced in our bodies help fight inflammation and create new blood vessels, among other responsibilities, but the compounds are delicate and break down easily, making them difficult to study.
Bio & Medicine
May 20, 2024
0
1

Using hybrid nanotubes to enhance cancer treatment with intracellular protein delivery
The intracellular delivery of proteins is an important technique for unveiling the cellular functions, protein complex structure, and therapeutics. However, conventional delivery methods have several limitations.
Bio & Medicine
May 20, 2024
0
13

Nanocarriers loaded with DNA relieve back pain, repairs damaged disk in mice
Disk-related back pain may one day meet its therapeutic match: Gene therapy delivered by naturally derived nanocarriers that, a new study shows, repairs damaged disks in the spine and lowers pain symptoms in mice.
Bio & Medicine
May 16, 2024
0
8

Engineering a new color palette for single-molecule imaging
Researchers often study biomolecules such as proteins or amino acids by chemically attaching a "fluorophore," a sensitive molecule that absorbs and re-emits energy from light.
Bio & Medicine
May 15, 2024
0
20

Scientists from Prague are expanding the possibilities of using RNA in gene medicine
Dr. Petr Cígler and his collaborators are working on refining molecular systems for transporting ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules into cells. The question of how to effectively deliver RNA to a designated place in the body ...
Bio & Medicine
May 15, 2024
0
20

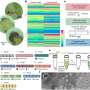
Multi-scale, nanomaterial-based ice inhibition platform enables full-cycle cryogenic protection for mouse oocytes
Safe and high-quality fertility preservation is of growing significance for women in clinical trials. Current primary methods for cryopreserving human oocytes are slow freezing and vitrification, but existing techniques pose ...
Bio & Medicine
May 15, 2024
0
1

Self-assembled Na-doped zinc oxide for the detection of lung cancer biomarker VOCs at low concentrations
Developing high-performance gas sensors for the detection of lung cancer markers at low concentrations is a crucial step towards achieving early lung cancer monitoring through breath tests. Metal oxide semiconductors (MOS) ...
Bio & Medicine
May 13, 2024
0
13

Exploration of individual colorectal cancer cell responses to H₂O₂ eustress
In a recent study published in the journal Science Bulletin, researchers from the Nano Life Science Institute (WPI-NanoLSI) at Kanazawa University utilized hopping probe scanning ion conductance microscopy (HPICM) and highly ...
Bio & Medicine
May 13, 2024
0
20

New gel breaks down alcohol in the body
Most alcohol enters the bloodstream via the mucous membrane layer of the stomach and the intestines. These days, the consequences of this are undisputed: even small amounts of alcohol impair people's ability to concentrate ...
Bio & Medicine
May 13, 2024
0
78

Nanoparticle plant virus treatment shows promise in fighting metastatic cancers in mice
An experimental treatment made from a plant virus is effective at protecting against a broad range of metastatic cancers in mice, according to a new study from the University of California San Diego.
Bio & Medicine
May 13, 2024
0
40

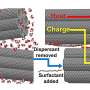
Research explores ways to mitigate the environmental toxicity of ubiquitous silver nanoparticles
Silver has long been used to thwart the spread of illness and in recent years silver nanoparticles have been incorporated into products ranging from sanitizers, odor-resistant clothes and washing machines to makeup, food ...
Bio & Medicine
May 11, 2024
0
56

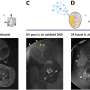
High-speed atomic force microscopy helps explain role played by certain biomolecules in DNA wrapping dynamics
In plants and animals, the basic packaging units of DNA, which carry genetic information, are the so-called nucleosomes. A nucleosome consists of a segment of DNA wound around eight proteins known as histones.
Bio & Medicine
May 10, 2024
0
26

Designer peptoids mimic nature's helices
Nature is filled with extraordinarily precise molecular shapes that fit together like a hand in glove. Proteins, for example, can assemble into a wide variety of well-defined shapes that grant them their function.
Bio & Medicine
May 10, 2024
0
216

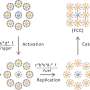
New DNA origami technique promises advances in medicine
A new technique in building DNA structures at a microscopic level has the potential to advance drug delivery and disease diagnosis, a study suggests.
Bio & Medicine
May 9, 2024
0
49

Enabling rapid screening of poly(2-oxazoline)-based nanomedicine through divergent synthesis
A research collaboration has devised a new way to quickly and reliably diversify the reactive end-groups on poly(2-oxazoline)s, a biocompatible polymer class.
Bio & Medicine
May 8, 2024
0
11
More news

Nanotech opens door to future of insulin medication

Bacteria 'nanowires' could help develop green electronics

Imaging technique shows new details of peptide structures
Other news
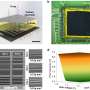
Researchers develop perovskite X-ray detector for medical imaging
How plants choose their mates and repel other suitors

Study decodes dimerization and antidepressant recognition at noradrenaline transporter

An endemic island falcon that plays
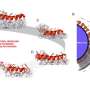
Engineers muffle invading pathogens with a 'molecular mask'

New device harnesses sweat power for fitness trackers

Genes provide hope for the survival of Arabia's last big cat