Study suggests that cells possess a hidden communication system
Cells constantly navigate a dynamic environment, facing ever-changing conditions and challenges. But how do cells swiftly adapt to these environmental fluctuations?

Cells constantly navigate a dynamic environment, facing ever-changing conditions and challenges. But how do cells swiftly adapt to these environmental fluctuations?
Cell & Microbiology
Apr 24, 2024
0
110

An intricate simulation performed by UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers using one of the world's most powerful supercomputers sheds new light on how proteins called SNAREs cause biological membranes to fuse.
Molecular & Computational biology
Apr 23, 2024
0
45
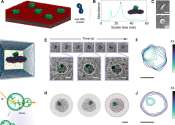
In a first demonstration of "electron videography," researchers have captured a microscopic moving picture of the delicate dance between proteins and lipids found in cell membranes. The technique can be used to study the ...
Bio & Medicine
Apr 22, 2024
0
246

Some pathogens hide inside human cells to enhance their survival. Researchers at the University of Basel, have uncovered a unique tactic certain bacteria use to spread in the body without being detected by the immune system. ...
Cell & Microbiology
Apr 22, 2024
0
44

Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin materials: 2D materials that are only 1 atom thick, or even just a couple of atoms. Think about graphene or ultra-thin silicon membrane for instance.
Nanophysics
Apr 18, 2024
0
17

Flow-through reactors packed with enzymes can produce certain chemicals in a gentle and careful way. However, their performance has so far been limited. A research team from the Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon and RWTH Aachen University ...
Bio & Medicine
Apr 18, 2024
0
70

Researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine have developed a powerful, new technique to generate "movies" of changing protein structures and speeds of up to 50 frames per second.
Molecular & Computational biology
Apr 17, 2024
0
33

Researchers have worked to uncover the mysteries surrounding a specific receptor protein associated with hearing. Professor Yunje Cho's research team from the Department of Life Sciences at Pohang University of Science and ...
Cell & Microbiology
Apr 16, 2024
0
3

Photosynthesis is a complex process, involving many pathways and puzzle pieces working together to keep the organism alive.
Plants & Animals
Apr 11, 2024
0
6

Voids, or empty spaces, exist within matter at all scales, from the astronomical to the microscopic. In a new study, researchers used high-powered microscopy and mathematical theory to unveil nanoscale voids in three dimensions. ...
Nanomaterials
Apr 11, 2024
0
583
A membrane is a layer of material which serves as a selective barrier between two phases and remains impermeable to specific particles, molecules, or substances when exposed to the action of a driving force. Some components are allowed passage by the membrane into a permeate stream, whereas others are retained by it and accumulate in the retentate stream.
Membranes can be of various thickness, with homogeneous or heterogeneous structure. Membrane can also be classified according to their pore diameter. According to IUPAC, there are three different types of pore size classifications: microporous (dp < 2nm), mesoporous (2nm < dp < 50nm) and macroporous (dp > 50nm). Membranes can be neutral or charged, and particles transport can be active or passive. The latter can be facilitated by pressure, concentration, chemical or electrical gradients of the membrane process. Membranes can be generally classified into three groups: inorganic, polymeric or biological membranes. These three types of membranes differ significantly in their structure and functionality.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA