New evidence for oceans of water deep in the Earth
Researchers from Northwestern University and the University of New Mexico report evidence for potentially oceans worth of water deep beneath the United States. Though not in the familiar liquid form—the ingredients for water are bound up in rock deep in the Earth's mantle—the discovery may represent the planet's largest water reservoir.
The presence of liquid water on the surface is what makes our "blue planet" habitable, and scientists have long been trying to figure out just how much water may be cycling between Earth's surface and interior reservoirs through plate tectonics.
Northwestern geophysicist Steve Jacobsen and University of New Mexico seismologist Brandon Schmandt have found deep pockets of magma located about 400 miles beneath North America, a likely signature of the presence of water at these depths. The discovery suggests water from the Earth's surface can be driven to such great depths by plate tectonics, eventually causing partial melting of the rocks found deep in the mantle.
The findings, to be published June 13 in the journal Science, will aid scientists in understanding how the Earth formed, what its current composition and inner workings are and how much water is trapped in mantle rock.
"Geological processes on the Earth's surface, such as earthquakes or erupting volcanoes, are an expression of what is going on inside the Earth, out of our sight," said Jacobsen, a co-author of the paper. "I think we are finally seeing evidence for a whole-Earth water cycle, which may help explain the vast amount of liquid water on the surface of our habitable planet. Scientists have been looking for this missing deep water for decades."
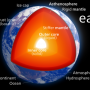
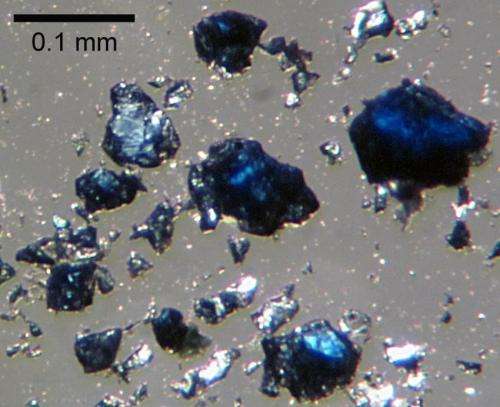
Scientists have long speculated that water is trapped in a rocky layer of the Earth's mantle located between the lower mantle and upper mantle, at depths between 250 miles and 410 miles. Jacobsen and Schmandt are the first to provide direct evidence that there may be water in this area of the mantle, known as the "transition zone," on a regional scale. The region extends across most of the interior of the United States.
Schmandt, an assistant professor of geophysics at the University of New Mexico, uses seismic waves from earthquakes to investigate the structure of the deep crust and mantle. Jacobsen, an associate professor of Earth and planetary sciences at Northwestern's Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences, uses observations in the laboratory to make predictions about geophysical processes occurring far beyond our direct observation.
The study combined Jacobsen's lab experiments in which he studies mantle rock under the simulated high pressures of 400 miles below the Earth's surface with Schmandt's observations using vast amounts of seismic data from the USArray, a dense network of more than 2,000 seismometers across the United States.
Jacobsen's and Schmandt's findings converged to produce evidence that melting may occur about 400 miles deep in the Earth. H2O stored in mantle rocks, such as those containing the mineral ringwoodite, likely is the key to the process, the researchers said.

"Melting of rock at this depth is remarkable because most melting in the mantle occurs much shallower, in the upper 50 miles," said Schmandt, a co-author of the paper. "If there is a substantial amount of H2O in the transition zone, then some melting should take place in areas where there is flow into the lower mantle, and that is consistent with what we found."
If just one percent of the weight of mantle rock located in the transition zone is H2O, that would be equivalent to nearly three times the amount of water in our oceans, the researchers said.
This water is not in a form familiar to us—it is not liquid, ice or vapor. This fourth form is water trapped inside the molecular structure of the minerals in the mantle rock. The weight of 250 miles of solid rock creates such high pressure, along with temperatures above 2,000 degrees Fahrenheit, that a water molecule splits to form a hydroxyl radical (OH), which can be bound into a mineral's crystal structure.
Schmandt and Jacobsen's findings build on a discovery reported in March in the journal Nature in which scientists discovered a piece of the mineral ringwoodite inside a diamond brought up from a depth of 400 miles by a volcano in Brazil. That tiny piece of ringwoodite—the only sample in existence from within the Earth—contained a surprising amount of water bound in solid form in the mineral.
"Whether or not this unique sample is representative of the Earth's interior composition is not known, however," Jacobsen said. "Now we have found evidence for extensive melting beneath North America at the same depths corresponding to the dehydration of ringwoodite, which is exactly what has been happening in my experiments."
For years, Jacobsen has been synthesizing ringwoodite, colored sapphire-like blue, in his Northwestern lab by reacting the green mineral olivine with water at high-pressure conditions. (The Earth's upper mantle is rich in olivine.) He found that more than one percent of the weight of the ringwoodite's crystal structure can consist of water—roughly the same amount of water as was found in the sample reported in the Nature paper.
"The ringwoodite is like a sponge, soaking up water," Jacobsen said. "There is something very special about the crystal structure of ringwoodite that allows it to attract hydrogen and trap water. This mineral can contain a lot of water under conditions of the deep mantle."
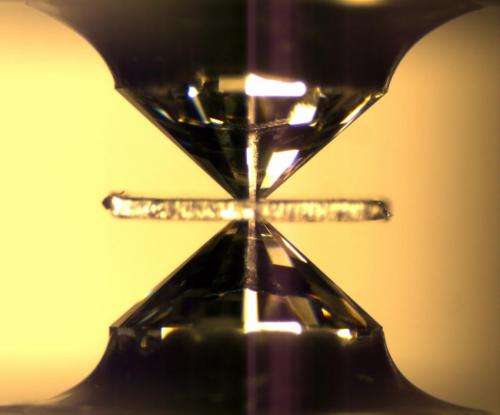
For the study reported in Science, Jacobsen subjected his synthesized ringwoodite to conditions around 400 miles below the Earth's surface and found it forms small amounts of partial melt when pushed to these conditions. He detected the melt in experiments conducted at the Advanced Photon Source of Argonne National Laboratory and at the National Synchrotron Light Source of Brookhaven National Laboratory.
Jacobsen uses small gem diamonds as hard anvils to compress minerals to deep-Earth conditions. "Because the diamond windows are transparent, we can look into the high-pressure device and watch reactions occurring at conditions of the deep mantle," he said. "We used intense beams of X-rays, electrons and infrared light to study the chemical reactions taking place in the diamond cell."
Jacobsen's findings produced the same evidence of partial melt, or magma, that Schmandt detected beneath North America using seismic waves. Because the deep mantle is beyond the direct observation of scientists, they use seismic waves—sound waves at different speeds—to image the interior of the Earth.
"Seismic data from the USArray are giving us a clearer picture than ever before of the Earth's internal structure beneath North America," Schmandt said. "The melting we see appears to be driven by subduction—the downwelling of mantle material from the surface."
The melting the researchers have detected is called dehydration melting. Rocks in the transition zone can hold a lot of H2O, but rocks in the top of the lower mantle can hold almost none. The water contained within ringwoodite in the transition zone is forced out when it goes deeper (into the lower mantle) and forms a higher-pressure mineral called silicate perovskite, which cannot absorb the water. This causes the rock at the boundary between the transition zone and lower mantle to partially melt.
"When a rock with a lot of H2O moves from the transition zone to the lower mantle it needs to get rid of the H2O somehow, so it melts a little bit," Schmandt said. "This is called dehydration melting."
"Once the water is released, much of it may become trapped there in the transition zone," Jacobsen added.
Just a little bit of melt, about one percent, is detectible with the new array of seismometers aimed at this region of the mantle because the melt slows the speed of seismic waves, Schmandt said.
More information: Dehydration melting at the top of the lower mantle, Science, 2014. www.sciencemag.org/lookup/doi/ … 1126/science.1253358
Provided by Northwestern University