NASA sees warm sea surface helped strengthen Tropical Storm 30W
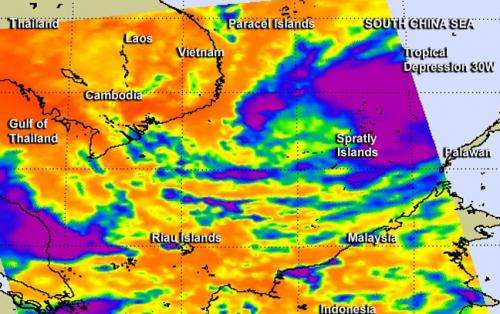
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the South China Sea and revealed that warm sea surface temperatures and low wind shear enabled Tropical Depression 30W to strengthen into a tropical storm.
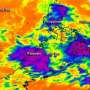
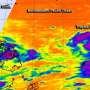
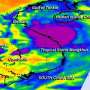
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm 30W on Nov. 5 at 0611 UTC/1:11 a.m. EDT as it was making its way west through the South China Sea. The infrared AIRS data provides valuable cloud top temperature data that indicates how high the thunderstorms are the make up the tropical cyclone. Some of those thunderstorms mostly north of the storm's center were high into the troposphere where air temperatures were colder than -63F/-52C. Cloud top temperatures in that range indicate that the thunderstorms have the potential to drop heavy rainfall.
AIRS infrared data also revealed that the sea surface temperatures are warm in the area of the South China Sea where TD30W is moving. Warm sea surface temperatures over 26.6C/80F are needed to maintain a tropical cyclone's intensity and those in the path of TD30W are warmer than that, enabling the storm to intensify through increased evaporation.
On Nov. 5 at 1500 UTC/10 a.m. EDT, Tropical Storm 30W or TS30W had maximum sustained winds near 35 knots/40 mph/64.8 kph. TS30W was located approximately 507 nautical miles/ 583.4 miles/939 km east of Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, near 11.0 north and 114.5 east. TS30W was moving west at 16 knots/18.4 mph/29.6 kph.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center forecast predicts that TS30W will make landfall as a tropical storm in southern Vietnam near the city of Nha Trang on Nov. 6 around 1200 UTC Universal Time./7 p.m. Vietnam local time.
Provided by NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center