This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
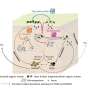
Comparison of four methods on drying efficiency and physicochemical properties of chicken meat
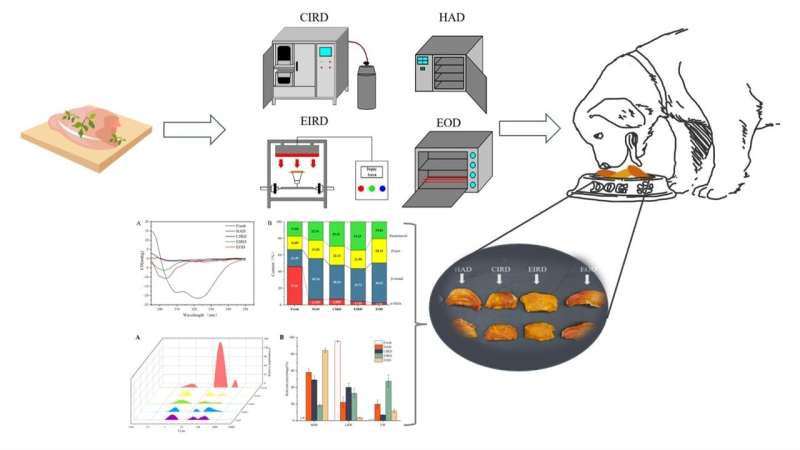
Chicken breast jerky (CBJ) is a popular pet food due to its high crude protein content and long shelf life. In the production of CBJ, the drying process is a crucial step. However, the physicochemical and functional properties of CBJ depend on the drying method used.
The main drying methods currently used for CBJ are hot air drying (HAD) and electric oven drying (EOD). To preserve the CBJ product's nutritional value and reduce the formation of heterocyclic amines, the processing temperature for HAD and EOD is limited to 55–65°C.
In HAD, the heated air is circulated around the food via internal fans, facilitating convection circulation. In contrast, EOD uses stainless steel tubes heated to raise the temperature of the air inside the equipment, thereby dehydrating the food materials. Both HAD and EOD offer advantages such as low equipment cost and simple operating processes. However, their drawbacks include low energy efficiency and long drying time, which may lead to a decline in the quality of the final jerky product.
In a new study conducted by researchers from Jiangsu University in Zhenjiang, China, four drying methods, HAD, EOD catalytic infrared drying (CIRD) and electric infrared drying (EIRD), were used to prepare dried chicken breast. The drying efficiencies of the different methods and their effects on physico-chemical properties, pet food applications, energy consumption and costs were systematically compared.
"We observed that CIRD and EOD yielded a better color in the final product, while the EIRD treatment resulted in the highest degree of denaturation of the chicken breast jerky proteins," shares the study's first author Rui Zhu.
"In terms of chemical properties, the higher malondialdehyde content of CIRD and EIRD indicated higher fat oxidation in IR-treated chicken meat, which is also associated with an increase in the content of free fatty acids."
Furthermore, the researchers found that arachidonic, linolenic and oleic acids were positively correlated with the content of important flavor compounds in the jerky. In terms of pet food preferences, CIRD and EIRD products were more well-received by pets. Energy and cost assessments also indicated that CIRD is more energy and cost-efficient compared to other drying methods.
Nonetheless, despite its advantages, CIRD still faces the challenge of high equipment costs in contrast to other traditional drying methods, requiring further industrial applications to solve.
The study's findings are published in the journal Food Physics.
More information: Rui Zhu et al, Comparison of four drying methods in terms of the drying efficiency and physicochemical properties of chicken meat, Food Physics (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.foodp.2024.100010
Provided by KeAi Communications Co., Ltd.