Toxin from salmonid fish has potential to treat cancer
Pathogenic bacteria develop killer machines that work very specifically and highly efficiently. Scientists from the University of Freiburg have solved the molecular mechanism of a fish toxin that could be used in the future as a medication to treat cancer. The scientists have now published their research in the journal Nature Communications.
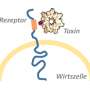
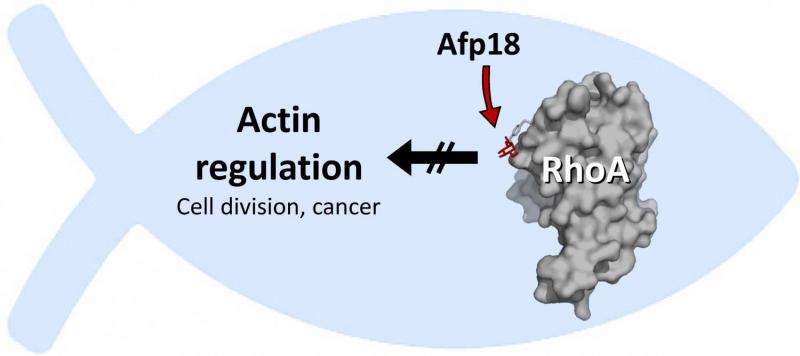
The Yersinia species of pathogens can cause the bubonic plague and serious gastrointestinal infections in humans. The pharmacologist Dr. Thomas Jank and his fellow researchers in the research group led by Prof. Dr. Dr. Klaus Aktories at the University of Freiburg studied a pathogen of the Yersinia family (Yersinia ruckeri). This pathogen causes redmouth disease in Salmonidae, which includes salmon and trout, resulting in large financial losses in the fish industry. The research group was able to identify a toxin injection machine in the Y. ruckeri genome. The structure of this machine resembles that of viruses that normally attack bacteria. The group demonstrated that the toxin Afp18 in this injection machine is an enzyme that deactivates the switch protein RhoA. RhoA is responsible for many vital processes in the cells of humans and fish. For example, it controls the building up and breaking down of actin filaments. These filaments are not only necessary for cell division, but also for the spreading of tumour metastases in the body.
In close collaboration with the developmental biologist Prof. Dr. Wolfgang Driever, also from the University of Freiburg, the research group injected the toxin Afp18 into zebra fish embryos. The result was that cell division was blocked, and the fish embryos did not develop. The toxin caused the actin filaments in the fish cells to collapse. This is because the Afp18 attaches a sugar molecule, an N-acetylglucosamine, onto the amino acid tyrosine in RhoA. According to the scientists, this is a very unusual reaction in nature. The team was able to shed light on this mechanism at the atomic level through the X-ray analysis of Afp18-modified RhoA crystals. For this, they collaborated with Prof. Dr. Daan von Aalten from the University of Dundee, Scotland. Rho-regulatory proteins are involved in the growth of cancer, especially metastasis. For this reason, the researchers from the University of Freiburg believe that this fish toxin has great therapeutic potential in cancer treatment.

More information: Nature Communications 6, Article number: 7807 DOI: 10.1038/ncomms8807
Journal information: Nature Communications
Provided by Centre for Biological Signalling Studies