Holes in gold enhance molecular sensing
Non-metallic mesoporous structures have already demonstrated potential for applications in gas storage, separation, catalysis, ion-exchange, sensing, polymerization and drug delivery. Metal mesoporous films could have fascinating and useful optical properties as they are effectively the inverse of nanoparticle arrays. Now for the first time a collaboration of researchers in Japan, Turkey, Korea and Sweden demonstrate a simple approach for producing metal films with regular tuneable mesopores, and show their potential for high-sensitivity optical detection.
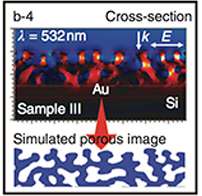
When light is incident on nanostructures of noble metals such as gold, the electrons oscillate collectively – a so-called plasmon – and this greatly enhances the electromagnetic field close by. According to Babinet's principle in optics, the inverse structure – a mesoporous film – should lead to similar local electromagnetic field enhancements, but as Yamauchi and his colleagues point out in their report, controlling gold crystal growth well enough to produce mesoporous films has so far been difficult.
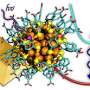
The success of their approach relies on electrochemistry and micelle self-assembly. They dissolve hydrogen gold chloride (or chloroauric acid, HAuCl4) and polystyrene-block-poly(oxyethylene) in a solution of tetrahydrofuran, which leads to the formation of micelles with a polystyrene core and polyoxyethylene shell. The micelles reduce the AuCl4- ions so that gold deposits on the micelles. The result is highly regular gold mesopores with a size that can be tuned by varying the concentrations of the HAuCl4 and polystyrene-block-poly(oxyethylene).
Calculations showed that hotspots of high electric field enhancement indeed exist in the pores of the structure, and the plasmon resonances can be tuned by changing the pore size. Further experiments confirmed the surface enhancement of protein spectral signatures, known as surface enhanced Raman scattering. The researchers conclude, "The electrochemical approach is widely applicable to embed uniform mesopores in other metal and alloy systems, which are generally difficult to be synthesized."
More information: "Electrochemical synthesis of mesoporous gold films toward mesospace-stimulated optical properties." Nature Communications DOI: 10.1038/ncomms7608
Journal information: Nature Communications
Provided by National Institute for Materials Science