The purification and characterization of ATP synthase complexes from the mitochondria of four fungal species
ATP, the fuel of life, is produced in mitochondria of living cells by a molecular machine, the ATP synthase. We have isolated the machines from four fungal species, compared their stabilities and identified the proteins from which they are constructed.
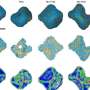
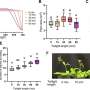
The ATP synthases have been isolated by affinity chromatography from the mitochondria of the fungal species, Yarrowia histolytica, Pichia pastoris, Pichia angusta and Saccharomyces cerevisae. The subunit compositions of the purified enzyme complexes depended upon the detergent used to solubilise and purify the complex, and the presence or absence of exogenous phospholipids.
All four enzymes purified in the presence of n-dodecyl-β-D-maltoside had a complete complement of core subunits involved directly in the synthesis of ATP, but they were deficient to different extents in their supernumerary membrane subunits. In contrast, the enzymes from P. angusta and S. cerevisiae purified in the presence of n-decyl-β-maltose neopentyl glycol and the phospholipids 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine, 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine, cardiolipin and 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-[phospho-rac-(1-glycerol)] had a complete complement of core subunits and also contained all the known supernumerary membrane subunits, e, f, g, j, k and ATP8 (or Aap1), plus an additional new membrane component named subunit l, related in sequence to subunit k.
The catalytic domain of the enzyme from P. angusta was more resistant to thermal denaturation than the enzyme from S. cerevisiae, but less stable than the catalytic domain of the bovine enzyme, but the stator and the integrity of the transmembrane proton pathway were most stable in the enzyme from P. angusta. The P. angusta enzyme provides a suitable source of enzyme for studying the structure of the membrane domain and properties associated with that sector of the enzyme complex.
More information: "The purification and characterization of ATP synthase complexes from the mitochondria of four fungal species." Sidong Liu, Thomas J Charlesworth, John V Bason, Martin G Montgomery, Michael E Harbour, Ian M. Fearnley and John E Walker Biochem. J. (2015) DOI: 10.1042/BJ20150197
Provided by MRC Mitochondrial Biology Unit