Emerald ash borer confirmed as threat to white fringetree

The emerald ash borer (Agrilus planipennis), also known as EAB, is an invasive insect pest from Asia that has killed millions of trees in the United States and Canada and has caused billions of dollars of damage since it was discovered in 2002. Fortunately, its damage has been limited to ash trees—or so we thought.
During the summer and fall of 2014, Dr. Don Cipollini, a professor at Wright State University, found evidence that the EAB can also attack white fringetree (Chionanthus virginicus), a species native to the southeastern United States that is planted ornamentally. His observations are described in an article published in the Journal of Economic Entomology called "White Fringetree as a Novel Larval Host for Emerald Ash Borer".
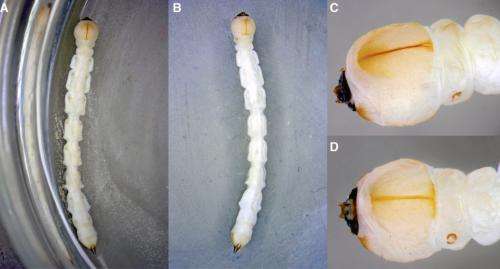
While examining white fringetrees in Yellow Springs, Ohio, Dr. Cipollini found external symptoms of emerald ash borer attacks, including the presence of adult exit holes, canopy dieback, bark splitting, and other deformities. After removing the bark from one of the trees, he found evidence that at least three generations of emerald ash borer larvae had used the tree, and he saw several live larvae that were actively feeding. In addition, he found a dead adult that has been confirmed as emerald ash borer. Additional white fringetrees exhibiting evidence of emerald ash borer attack were also found in Springfield and Dayton, Ohio.
"It appears that emerald ash borer is eating more than ash trees," Cipollini said. "It may have a wider host range than we ever thought in the first place, or it is adapting to utilize new hosts. This biological invasion is having drastic ecological and economic consequences, and you can't always predict what's going to happen."
The borers attack trees by laying eggs on the bark. The serpentine feeding galleries of the larvae inside the bark disrupt the flow of nutrients and water and starve the tree.
White fringetree, a relative of ash, is a deciduous shrub or small tree that can grow up to 30 feet tall. It has white flowers and a purple, olive-like fruit, and is growing in popularity as an ornamental. It is known for its relative lack of pest and disease problems, and until now has never been reported as a host to wood borers related to emerald ash borer.
More information: Journal of Economic Entomology, jee.oxfordjournals.org/lookup/ … i/10.1093/jee/tou026
Journal information: Journal of Economic Entomology
Provided by Entomological Society of America
















