Researcher achieves breakthrough in building efficient single-photon detector
Ultrafast, efficient, and reliable single-photon detectors are among the most sought-after components in photonics and quantum communication, which have not yet reached maturity for practical application. Physicist Dr. Wolfram Pernice of the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT), in cooperation with colleagues at Yale University, Boston University, and Moscow State Pedagogical University, achieved the decisive breakthrough by integrating single-photon detectors with nanophotonic chips. The detector combines near-unity detection efficiency with high timing resolution and has a very low error rate. The results have been published by Nature Communications.
Without reliable detection of single photons, it is impossible to make real use of the latest advances in optical data transmission or quantum computation; it is like having no analog-digital converter in a conventional computer to determine whether the applied voltage stands for 0 or 1. Although a number of different single-photon detector models have been developed over the past few years, thus far, none have provided satisfactory performance.
Several new ideas and advanced developments went into the prototype developed within the "Integrated Quantum Photonics" project at the DFG Center of Functional Nanostructures (CFN). The new single-photon detector, tested in the telecommunications wavelength range, achieves a previously unattained detection efficiency of 91%.
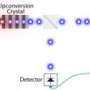
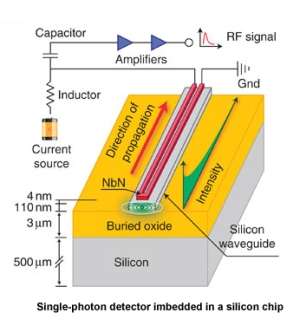
The detector was realized by fabricating superconducting nanowires directly on top of a nanophotonic waveguide. This geometry can be compared to a tube that conducts light, around which a wire in a superconducting state is wound and, as such, has no electric resistivity. The nanometer-sized wire made of niobium nitride absorbs photons that propagate along the waveguide. When a photon is absorbed, superconductivity is lost, which is detected as an electric signal. The longer the tube, the higher is the detection probability. The lengths involved are in the micrometer range.
A special feature of the detector is its direct installation on the chip, which allows for it to be replicated at random. The single-photon detectors built thus far were stand-alone units, which were connected to chips with optical fibers. Arrangements of that type suffer from photons being lost in the fiber connection or being absorbed in other ways. These loss channels do not exist in the detector that is now fully embedded in a silicon photonic circuit. In addition to high detection efficiency, this gives rise to a remarkably low dark count rate. Dark counts arise when a photon is detected erroneously: for instance, because of a spontaneous emission, an alpha particle, or a spurious field. The new design also provides ultrashort timing jitter of 18 picoseconds, which is 18 times 10-12 seconds.
The novel solution also makes it possible to integrate several hundreds of these detectors on a single chip. This is a basic precondition for future use in optical quantum computers.
The detector demonstrated in this study was designed to work at wavelengths in the Telekom bandwidth. The same detector architecture can also be used for wavelengths in the range of visible light. This would allow the principle to be employed in analyses of all structures that emit little light, i.e., photons, such as single molecules or bacteria.
More information: doi:10.1038/ncomms2307
Journal information: Nature Communications
Provided by Karlsruhe Institute of Technology